with Choice Timber, each for Regression and Classification, we’ll proceed to make use of the precept of Choice Timber right this moment.
And this time, we’re in unsupervised studying, so there are not any labels.
The algorithm is known as Isolation Forest, and the thought is to construct many resolution bushes to type a forest. The precept is to detect anomalies by isolating them.
To maintain every part simple to know, let’s take a quite simple instance dataset that I created myself:
1, 2, 3, 9
(And since the chief editor of TDS jogged my memory about authorized particulars about mentioning the supply of the info, let me state this correctly: this dataset is absolutely copyrighted on my own. It’s a four-point dataset that I handcrafted, and I’m comfortable to grant everybody the best to make use of it for instructional functions.)
The aim right here is easy: discover the anomaly, the intruder.
I do know you already see which one it’s.
As at all times, the thought is to show this into an algorithm that may detect it mechanically.
Anomaly Detection within the Basic ML Framework
Earlier than going additional, allow us to take one step again and see the place anomaly detection sits within the greater image.
On the left, now we have supervised studying, with labeled information and two primary varieties:
- Regression when the goal is numerical
- Classification when the goal is categorical
That is the place we used Choice Timber to date.
On the best, now we have unsupervised studying, with no labels.
We don’t predict something. We merely manipulate the observations (clustering and anomaly detection) or manipulate the options (dimensionality discount, and different strategies).
Dimensionality discount manipulates the options. Regardless that it sits within the “unsupervised” class, its aim is kind of totally different from the others. Because it reshapes the options themselves, it nearly seems like function engineering.
For observation-level strategies, now we have two potentialities:
- Clustering: group observations
- Anomaly detection: assign a rating to every remark
In observe, some fashions can do the 2 on the similar time. For instance, the k-means is able to detecting anomalies.
Isolation Forest is just for Anomaly Detection, and never clustering.
So, right this moment, we’re precisely right here:
Unsupervised studying → Clustering / Anomaly detection → Anomaly detection
The Painful Half: Constructing Timber in Excel
Now we start the implementation in Excel, and I’ve to be trustworthy: this half is basically painful…
It’s painful as a result of we have to construct many small guidelines, and the formulation usually are not simple to pull. This is likely one of the limitations of Excel when the mannequin is predicated on choices. Excel is nice when the formulation look the identical for each row. However right here, every node within the tree follows a distinct rule, so the formulation don’t generalize simply.
For Choice Timber, we noticed that with a single break up, the formulation labored. However I finished there on function. Why? As a result of including extra splits in Excel turns into sophisticated. The construction of a call tree shouldn’t be naturally “drag-friendly”.
Nevertheless, for Isolation Forest, now we have no alternative.
We have to construct a full tree, all the way in which down, to see how every level is remoted.
In case you, pricey readers, have concepts to simplify this, please contact me.
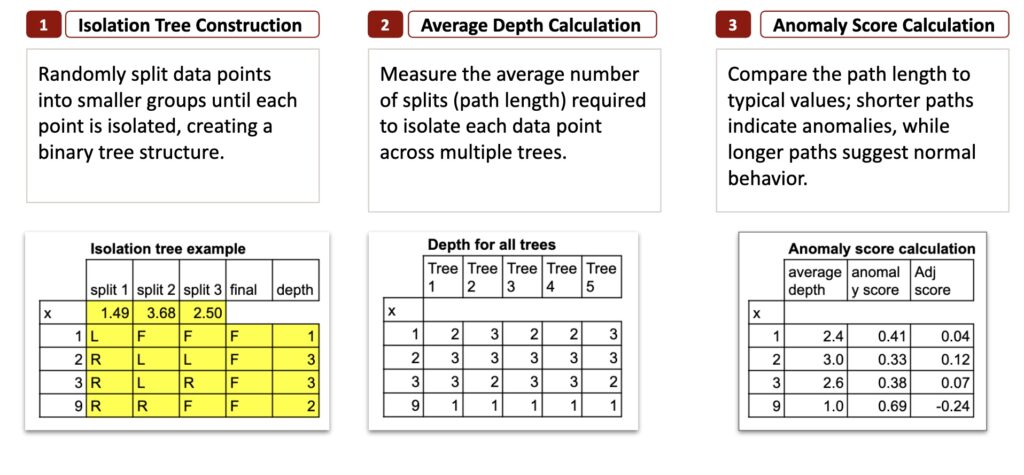
Isolation Forest in 3 Steps
Regardless that the formulation usually are not simple, I attempted my greatest to construction the strategy. Right here is the complete technique in simply three steps.

1. Isolation Tree Building
We begin by creating one isolation tree.
At every node, we choose a random break up worth between the minimal and most of the present group.
This break up divides the observations into “left” (L) and “proper” (R).
When an remark turns into remoted, I mark it as F for “Ultimate”, that means it has reached a leaf.
By repeating this course of, we get hold of a full binary tree the place anomalies are typically remoted in fewer steps. For every remark, we are able to then depend its depth, which is just the variety of splits wanted to isolate it.

2. Common Depth Calculation
One tree shouldn’t be sufficient. So we repeat the identical random course of a number of occasions to construct a number of bushes.
For every information level, we depend what number of splits have been wanted to isolate it in every tree.
Then we compute the common depth (or common path size) throughout all bushes.
This offers a steady and significant measure of how simple it’s to isolate every level.
At this level, the common depth already provides us a strong indicator:
the decrease the depth, the extra probably the purpose is an anomaly.
A brief depth means the purpose is remoted in a short time, which is a signature of an anomaly.
A protracted depth means the purpose behaves like the remainder of the info, as a result of they keep grouped collectively, and usually are not simple to separate.
In our instance, the rating makes good sense.
- First, 9 is the anomaly, with the common depth of 1. For all 5 bushes, one break up is sufficient to isolate it. (Though, this isn’t at all times the case, you may take a look at it your self.)
- For the opposite three observations, the depth is comparable, and noticeably bigger. And the very best rating is attributed to 2, which sits in the midst of the group, and that is precisely what we count on.
If at some point you need to clarify this algorithm to another person, be happy to make use of this dataset: simple to recollect and intuitive for example. And please, don’t forget to say my copyright on it!

3. Anomaly Rating Calculation
The ultimate step is to normalize the common depth, to offer a normal anomaly rating, between 0 and 1.
Saying that an remark has a median depth of n doesn’t imply a lot by itself.
This worth relies on the entire variety of information factors, so we can not interpret it straight as “regular” or “anomalous”.
The concept is to check the common path size of every level to a typical worth anticipated below pure randomness. This tells us how stunning (or not) the depth actually is.
We’ll see the transformation later, however the aim is easy:
flip the uncooked depth right into a relative rating that is smart with none context.
Brief depths will naturally grow to be scores near 1 (anomalies),
and lengthy depths will grow to be scores near 0 (regular observations).
And eventually, some implementations regulate the rating in order that it has a distinct that means: constructive values point out regular factors, and unfavorable values point out anomalies. That is merely a metamorphosis of the unique anomaly rating.
The underlying logic doesn’t change in any respect: brief paths nonetheless correspond to anomalies, and lengthy paths correspond to regular observations.

Isolation Tree Constructing
So that is the painful half.
Fast Overview
I created a desk to seize the totally different steps of the tree-building course of.
It isn’t common, and it’s not completely structured, however I attempted my greatest to make it readable.
And I’m not certain that every one the formulation generalized effectively.

- Get the minimal and most values of the present group.
- Generate a random break up worth between this min and max.
- Break up the observations into left (L) and proper (R).
- Depend what number of observations fall into L and R.
- If a bunch comprises solely one remark, mark it as F (Ultimate) and cease for that department.
- Repeat the method for each non-final group till all observations are remoted.
That is the complete logic of constructing one isolation tree.
Developed Clarification
We start with all of the observations collectively.
Step one is to have a look at the minimal and most of this group. These two values outline the interval the place we are able to make a random reduce.
Subsequent, we generate a random break up worth someplace between the min and max. In contrast to resolution bushes, there is no such thing as a optimization, no criterion, no impurity measure. The break up is only random.
We are able to use RAND in Excel, as you may see the in following screenshot.

As soon as now we have the random break up, we divide the info into two teams:
- Left (L): observations lower than or equal to the break up
- Proper (R): observations higher than the break up
That is merely achieved by evaluating the break up with the observations with IF formulation.

After the break up, we depend what number of observations went to every facet.
If one in every of these teams comprises just one remark, this level is now remoted.
We mark it as F for “Ultimate”, that means it sits in a leaf and no additional splitting is required for that department.
The VLOOKUP is to get the observations which have 1 on its facet, from the desk of the counts.

For all different teams that also include a number of observations, we repeat precisely the identical course of.
We cease solely when each remark is remoted, that means every one seems in its personal remaining leaf. The complete construction that emerges is a binary tree, and the variety of splits wanted to isolate every remark is its depth.
Right here, we all know that 3 splits are sufficient.
On the finish, you get the ultimate desk of 1 absolutely grown isolation tree.
Anomaly Rating Calculation
The half about averaging the depth is simply repeating the identical course of, and you may copy paste.
Now, I’ll give extra particulars in regards to the anomaly rating calculation.
Normalization issue
To compute the anomaly rating, Isolation Forest first wants a normalizing issue referred to as c(n).
This worth represents the anticipated depth of a random level in a random binary search tree with n observations.
Why do we want it?
As a result of we wish to evaluate the precise depth of some extent to the typical depth anticipated below randomness.
Some extent that’s remoted a lot sooner than anticipated is probably going an anomaly.
The formulation for c(n) makes use of harmonic numbers.
A harmonic quantity H(okay) is roughly:

the place γ = 0.5772156649 is the Euler–Mascheroni fixed.
Utilizing this approximation, the normalizing issue turns into:

Then we are able to calculate this quantity in Excel.

As soon as now we have c(n), the anomaly rating is:

the place h(x) is the common depth wanted to isolate the purpose throughout all bushes.
If the rating is near 0, the purpose is regular
If the rating is near 1, the purpose is an anomaly
So we are able to rework the depths into scores.

Lastly, for the adjusted rating, we are able to use an offset, that’s the common worth of the anomaly scores, and we translate.

Extra Parts in Actual Algorithm
In observe, Isolation Forest features a few additional steps that make it extra strong.
1. Select a subsample of the info
As an alternative of utilizing the total dataset for each tree, the algorithm picks a small random subset.
This reduces computation and provides variety between bushes.
It additionally helps forestall the mannequin from being overwhelmed by very giant datasets.
So plainly a reputation like “Random Isolation Forest” is extra appropriate, proper?
2. Choose a random function first
When constructing every break up, Isolation Forest doesn’t at all times use the identical function.
It first selects a function at random, then chooses a random break up worth inside that function.
This makes the bushes much more numerous and helps the mannequin work effectively on datasets with many variables.
These easy additions make Isolation Forest surprisingly highly effective for real-world purposes.
That is once more what a “Random Isolation Forest” would do, this identify is unquestionably higher!
Benefits of Isolation Forest
In contrast with many distance-based fashions, Isolation Forest has a number of essential benefits:
- Works with categorical options
Distance-based strategies wrestle with classes, however Isolation Forest can deal with them extra naturally. - Handles many options simply
Excessive-dimensional information shouldn’t be an issue.
The algorithm doesn’t depend on distance metrics that break in excessive dimensions. - No assumptions about distributions
There is no such thing as a want for normality, no density estimation, no distances to compute. - Scales effectively to excessive dimensions
Its efficiency doesn’t collapse when the variety of options grows. - Very quick
Splitting is trivial: choose a function, choose a random worth, reduce.
No optimization step, no gradient, no impurity calculation.
Isolation Forest additionally has a really refreshing mind-set:
As an alternative of asking “What ought to regular factors appear to be?”,
Isolation Forest asks, “How briskly can I isolate this level?”
This straightforward change of perspective solves many difficulties of classical anomaly detection.
Conclusion
Isolation Forest is an algorithm that appears sophisticated from the skin, however when you break it down, the logic is definitely quite simple.
The Excel implementation is painful, sure. However the thought shouldn’t be.
And when you perceive the thought, every part else turns into a lot simpler: how the bushes work, why the depth issues, how the rating is computed, and why the algorithm works so effectively in observe.
Isolation Forest doesn’t attempt to mannequin “regular” habits. As an alternative, it asks a very totally different query: how briskly can I isolate this remark?
This small change of perspective solves many issues that distance-based or density-based fashions wrestle with.