, we’ve explored a lot of the core machine studying fashions, organized into three main households: distance- and density-based fashions, tree- or rule-based fashions, and weight-based fashions.
Up up to now, every article targeted on a single mannequin, educated by itself. Ensemble studying adjustments this attitude fully. It’s not a standalone mannequin. As an alternative, it’s a approach of combining these base fashions to construct one thing new.
As illustrated within the diagram under, an ensemble is a meta-model. It sits on high of particular person fashions and aggregates their predictions.
Voting: the only ensemble thought
The best type of ensemble studying is voting.
The concept is sort of trivial: prepare a number of fashions, take their predictions, and compute the typical. If one mannequin is fallacious in a single path and one other is fallacious in the other way, the errors ought to cancel out. A minimum of, that’s the instinct.
On paper, this sounds cheap. In follow, issues are very totally different.
As quickly as you attempt voting on actual fashions, one truth turns into apparent: voting shouldn’t be magic. Merely averaging predictions doesn’t assure higher efficiency. In lots of circumstances, it truly makes issues worse.
The reason being easy. Once you mix fashions that behave very otherwise, you additionally mix their weaknesses. If the fashions don’t make complementary errors, averaging can dilute helpful construction as a substitute of reinforcing it.
To see this clearly, contemplate a quite simple instance. Take a choice tree and a linear regression educated on the identical dataset. The choice tree captures native, non-linear patterns. The linear regression captures a world linear pattern. Once you common their predictions, you don’t receive a greater mannequin. You receive a compromise that’s usually worse than every mannequin taken individually.

This illustrates an vital level: ensemble studying requires greater than averaging. It requires a method. A technique to mix fashions that really improves stability or generalization.
Furthermore, if we contemplate the ensemble as a single mannequin, then it have to be educated as such. Easy averaging presents no parameter to regulate. There’s nothing to study, nothing to optimize.
One doable enchancment to voting is to assign totally different weights to the fashions. As an alternative of giving every mannequin the identical significance, we might attempt to study which of them ought to matter extra. However as quickly as we introduce weights, a brand new query seems: how can we prepare them? At that time, the ensemble itself turns into a mannequin that must be fitted.
This remark leads naturally to extra structured ensemble strategies.
On this article, we start with one statistical strategy to resample the coaching dataset earlier than averaging: Bagging.
The instinct behind Bagging
What’s bagging?
The reply is definitely hidden within the identify itself.
Bagging = Bootstrap + Aggregating.
You may instantly inform {that a} mathematician or a statistician named it. 🙂
Behind this barely intimidating phrase, the concept is very simple. Bagging is about doing two issues: first, creating many variations of the dataset utilizing the bootstrap, and second, aggregating the outcomes obtained from these datasets.
The core thought is subsequently not about altering the mannequin. It’s about altering the knowledge.
Bootstrapping the dataset
Bootstrapping means sampling the dataset with substitute. Every bootstrap pattern has the identical dimension as the unique dataset, however not the identical observations. Some rows seem a number of instances. Others disappear.
In Excel, that is very straightforward to implement and, extra importantly, very straightforward to see.
You begin by including an ID column to your dataset, one distinctive identifier per row. Then, utilizing the RANDBETWEEN perform, you randomly draw row indices. Every draw corresponds to at least one row within the bootstrap pattern. By repeating this course of, you generate a full dataset that appears acquainted, however is barely totally different from the unique one.
This step alone already makes the concept of bagging concrete. You may actually see the duplicates. You may see which observations are lacking. Nothing is summary.
Under, you may see examples of bootstrap samples generated from the identical unique dataset. Every pattern tells a barely totally different story, despite the fact that all of them come from the identical knowledge.
These different datasets are the muse of bagging.

Bagging linear regression: understanding the precept
Bagging course of
Sure, that is most likely the primary time you hear about bagging linear regression.
In concept, there’s nothing fallacious with it. As we stated earlier, bagging is an ensemble technique that may be utilized to any base mannequin. Linear regression is a mannequin, so technically, it qualifies.
In follow, nevertheless, you’ll shortly see that this isn’t very helpful.
However nothing prevents us from doing it. And exactly as a result of it isn’t very helpful, it makes for a superb studying instance. So allow us to do it.
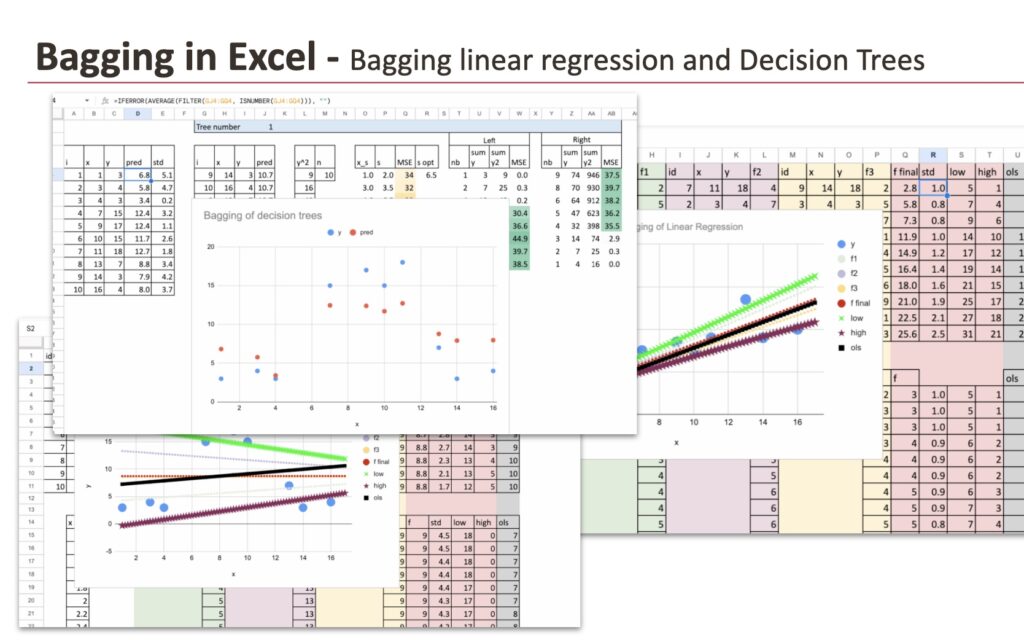
For every bootstrap pattern, we match a linear regression. In Excel, that is simple. We will straight use the LINEST perform to estimate the coefficients. Every coloration within the plot corresponds to at least one bootstrap pattern and its related regression line.
Up to now, every part behaves precisely as anticipated. The traces are shut to one another, however not similar. Every bootstrap pattern barely adjustments the coefficients, and subsequently the fitted line.

Now comes the important thing remark.
It’s possible you’ll discover that one extra mannequin is plotted in black. This one corresponds to the usual linear regression fitted on the unique dataset, with out bootstrapping.
What occurs after we examine it to the bagged fashions?
After we common the predictions of all these linear regressions, the ultimate result’s nonetheless a linear regression. The form of the prediction doesn’t change. The connection between the variables stays linear. We didn’t create a extra expressive mannequin.
And extra importantly, the bagged mannequin finally ends up being very near the usual linear regression educated on the unique knowledge.
We will even push the instance additional by utilizing a dataset with a clearly non-linear construction. On this case, every linear regression fitted on a bootstrap pattern struggles in its personal approach. Some traces tilt barely upward, others downward, relying on which observations had been duplicated or lacking within the pattern.

Bootstrap confidence intervals
From a prediction efficiency standpoint, bagging linear regression shouldn’t be very helpful.
Nonetheless, bootstrapping stays extraordinarily helpful for one vital statistical notion: estimating the confidence interval of the predictions.
As an alternative of wanting solely on the common prediction, we will take a look at the distribution of predictions produced by all of the bootstrapped fashions. For every enter worth, we now have many predicted values, one from every bootstrap pattern.
A easy and intuitive technique to quantify uncertainty is to compute the normal deviation of those predictions. This normal deviation tells us how delicate the prediction is to adjustments within the knowledge. A small worth means the prediction is steady. A big worth means it’s unsure.
This concept works naturally in Excel. Upon getting all of the predictions from the bootstrapped fashions, computing their normal deviation is simple. The outcome will be interpreted as a confidence band across the prediction.
That is clearly seen within the plot under. The interpretation is simple: in areas the place the coaching knowledge is sparse or extremely dispersed, the arrogance interval turns into vast, as predictions differ considerably throughout bootstrap samples.
Conversely, the place the information is dense, predictions are extra steady and the arrogance interval narrows.

Now, after we apply this to non-linear knowledge, one thing turns into very clear. In areas the place the linear mannequin struggles to suit the information, the predictions from totally different bootstrap samples unfold out rather more. The arrogance interval turns into wider.
This is a vital perception. Even when bagging doesn’t enhance prediction accuracy, it supplies helpful details about uncertainty. It tells us the place the mannequin is dependable and the place it isn’t.
Seeing these confidence intervals emerge straight from bootstrap samples in Excel makes this statistical idea very concrete and intuitive.

Bagging determination timber: from weak learners to a robust mannequin
Now we transfer to determination timber.
The precept of bagging stays precisely the identical. We generate a number of bootstrap samples, prepare one mannequin on every of them, after which combination their predictions.
I improved the Excel implementation to make the splitting course of extra computerized. To maintain issues manageable in Excel, we limit the timber to a single cut up. Constructing deeper timber is feasible, however it shortly turns into cumbersome in a spreadsheet.
Under, you may see two of the bootstrapped timber. In complete, I constructed eight of them by merely copying and pasting formulation, which makes the method simple and simple to breed.

Since determination timber are extremely non-linear fashions and their predictions are piecewise fixed, averaging their outputs has a smoothing impact.
Consequently, bagging naturally smooths the predictions. As an alternative of sharp jumps created by particular person timber, the aggregated mannequin produces extra gradual transitions.
In Excel, this impact may be very straightforward to watch. The bagged predictions are clearly smoother than the predictions of any single tree.

A few of you could have already heard of determination stumps, that are determination timber with a most depth of 1. That’s precisely what we use right here. Every mannequin is very simple. By itself, a stump is a weak learner.
The query right here is:
is a set of determination stumps adequate when mixed with bagging?
We’ll come again to this later in my Machine Studying “Creation Calendar”.
Random Forest: extending bagging
What about Random Forest?
That is most likely one of many favourite fashions amongst knowledge scientists.
So why not speak about it right here, even in Excel?
The truth is, what we’ve simply constructed is already very near a Random Forest!
To know why, recall that Random Forest introduces two sources of randomness.
- The primary one is the bootstrap of the dataset. That is precisely what we’ve already finished with bagging.
- The second is randomness within the splitting course of. At every cut up, solely a random subset of options is taken into account.
In our case, nevertheless, we solely have one characteristic. Which means there’s nothing to pick from. Function randomness merely doesn’t apply.
Consequently, what we receive right here will be seen as a simplified Random Forest.
As soon as this idea is obvious, extending the concept to a number of options is simply a further layer of randomness, not a brand new idea.
And it’s possible you’ll even ask, we will apply this precept to Linear Regression, and do a Random
Conclusion
Ensemble studying is much less about advanced fashions and extra about managing instability.
Easy voting isn’t efficient. Bagging linear regression adjustments little and stays principally pedagogical, although it’s helpful for estimating uncertainty. With determination timber, nevertheless, bagging really issues: averaging unstable fashions results in smoother and extra strong predictions.
Random Forest naturally extends this concept by including further randomness, with out altering the core precept. Seen in Excel, ensemble strategies cease being black packing containers and grow to be a logical subsequent step.
Thanks on your assist for my Machine Learning “Advent Calendar“.
Individuals normally speak rather a lot about supervised studying, however unsupervised studying is usually missed, despite the fact that it may well reveal construction that no label might ever present.
If you wish to discover these concepts additional, listed below are three articles that dive into highly effective unsupervised fashions.
An improved and extra versatile model of k-means.
In contrast to k-means, GMM permits clusters to stretch, rotate, and adapt to the true form of the information.
However when do k-means and GMM truly produce totally different outcomes?
Take a look at this text to see concrete examples and visible comparisons.
Local Outlier Factor (LOF)
A intelligent technique that compares every level’s native density to its neighbors to detect anomalies.
All of the Excel recordsdata can be found via this Kofi link. Your assist means rather a lot to me. The value will enhance through the month, so early supporters get the very best worth.