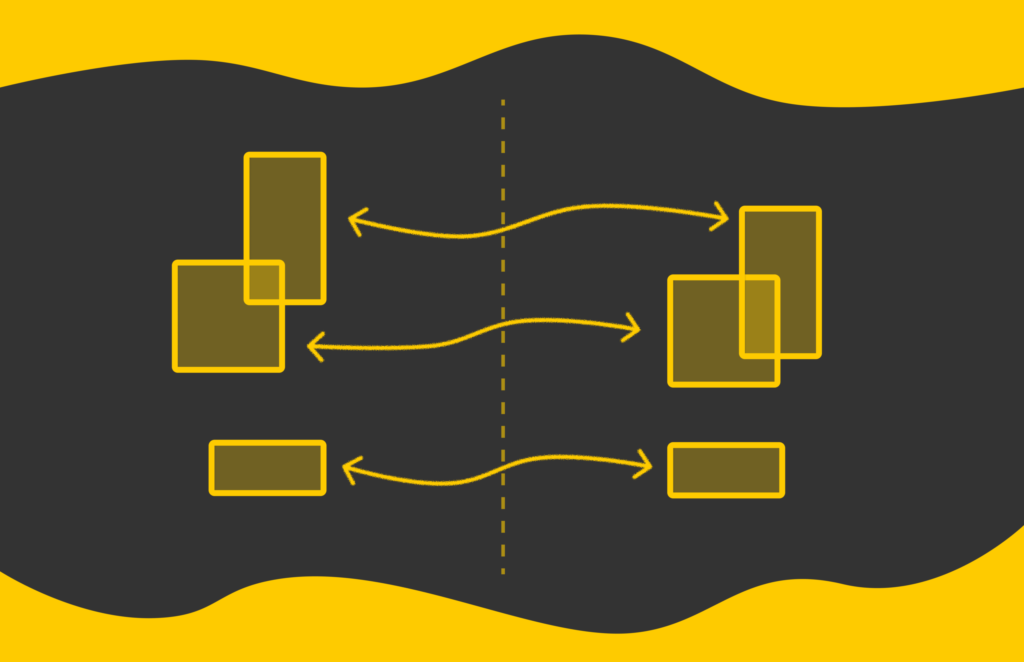
Multi-object monitoring (MOT) is a activity through which an algorithm should detect and observe a number of objects in a video. Most identified algorithms are primarily based on utilizing easy detectors (e.g. YOLO) designed for processing particular person photos. The general technique entails individually utilizing a detector on consecutive video frames after which matching the corresponding bounding bins throughout totally different frames that belong to the identical objects.
The core half that makes MOT algorithms totally different is how they carry out matching between video frames. They’ll consider a number of components to carry out matching:
- bounding field positions;
- occlusions (when bounding bins of a number of objects intersect with one another);
- object’s movement;
- bodily object similarity;
In some circumstances, for each pair of bounding bins on consecutive frames A and B, these traits are mixed right into a single quantity that describes the probability {that a} pair of bounding bins detected in frames A and B belongs to the identical object.
These values are calculated for all pairs of bounding bins in frames A and B. Then, the MOT algorithm makes an attempt to determine the absolute best matching between all bounding bins. Extra concretely, given n detected bounding bins in each frames A and B, the objective is to create a mapping between each bounding field from A to B in a manner that each bounding field is used solely as soon as.
Hungarian algorithm
The Hungarian algorithm is often studied in algorithms and knowledge construction programs. However, it additionally has functions in matching programs, and, particularly, is continuously used to resolve the tracklet matching drawback talked about above.
We’re going to research the workflow of the Hungarian algorithm in easier settings. As soon as we now have understood how it’s used, we can apply it to MOT issues as nicely simply.
The algorithm is known as Hungarian as a result of it’s “was largely primarily based on the sooner works of two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry” — Hungarian Algorithm | Wikipedia
Formulation
There exist many examples to show the Hungarian algorithm. I just like the one with employees and duties. Right here is the formulation:
There are n employees out there, and n duties should be accomplished by them. There may be details about the wage each employee receives for each activity. As for the corporate director, the issue consists of optimally assigning duties to employees given the next situations:
- each employee will get assigned just one activity;
- all duties get accomplished;
- the cash spent on salaries needs to be minimized.
We’re going to remedy this drawback by utilizing the next 4 x 4 value matrix for example:

Geometrically, given the matrix above, the target consists of selecting n matrix components in a way that there are not any repeating components in any row or column, and the whole sum of chosen components is minimal.
Thought
The Hungarian technique entails remodeling the preliminary value matrix into a brand new type that facilitates the answer search. For this, we are going to use a number of matrix transformations. Although the matrix will likely be modified, the issue will all the time stay equal, that means that the answer will nonetheless be the identical.
To maintain issues easy, we aren’t going to show right here mathematically why this or that matrix transformation maintains the issue invariant. As a substitute, we are going to present some logical ideas to clarify why the answer stays the identical.
Instance
1. Row & column discount
Step one consists of figuring out a minimal factor in each row of the matrix and subtracting it from every row. The concept right here is to get no less than one zero in each row. In observe, having extra zeros simplifies the issue.
Suppose that some quantity m is subtracted from a given row. Whereas the target worth (the whole minimized wage) modifications throughout the transformation (it decreases by m), the relative value between the assignments for a similar employee stays unchanged. Subsequently, the rating of options remained unchanged.
The analogous process is then carried out on columns: a minimal factor in each column is subtracted from that column.

After the primary two transformations, we get hold of a matrix with some zeros representing potential assignments.
The subsequent step consists of drawing the minimal variety of horizontal and vertical strains in a manner that they cross by all zeros within the matrix. Within the picture beneath, we will draw okay = 3 strains in whole to cowl all zeros.

If the variety of drawn strains equals the dimension n of the matrix, then we now have discovered an answer. The one step left in such a case is to decide on n zeros such that no zero is on the identical horizontal or vertical line as one other zero.
Since, in our instance, n ≠ okay, (the matrix dimension n = 4; the variety of drawn strains okay = 3), it means we should carry out an adjustment step.
2. Adjustment step
To this point, we now have drawn a number of strains, and we will classify the matrix components into three classes:
- Uncovered components;
- Lined components (solely as soon as);
- Nook components (components which are coated twice — horizontally and vertically).
The concept of the adjustment step consists of figuring out the minimal factor amongst uncovered components and subtracting it from all uncovered components. On the similar time, this worth will get added to all nook components.
In our instance, the minimal uncovered factor is 2. In consequence, we subtract 2 from all uncovered components (in pink) and a couple of from all nook components (in inexperienced).

Though it may not be apparent why the issue invariant stays maintained after the adjustment step, it may be mathematically confirmed that subtracting a quantity from all uncovered prices is equally compensated by its addition to all coated prices twice, which maintains the optimum resolution the identical.
This transformation was a single iteration of the adjustment step, which led us to a different equal matrix type. As earlier than, we carry out the examine to search out out if we will cowl all zeros utilizing solely n strains.

As we will see, this time we certainly have to attract okay = n = 4 strains to cowl all zeros. It signifies that we will lastly retrieve our resolution!
In any other case, if we might have drawn fewer than okay < 4 strains, we must always have repeated the adjustment step till the variety of strains turned okay = 4.
3. Answer retrieval
The one step left is to search out n zeros on totally different vertical and horizontal strains. If doing it manually, it’s higher to start out with strains which have fewer zeroes.
After discovering the positions of zeros within the matrix, we will change again to the unique matrix and select the preliminary components with the identical positions because the discovered zeros. And that would be the ultimate project!

The complexity of the Hungarian algorithm is O(n³), the place n is the matrix dimension.
The project drawback we now have simply seen will also be solved by linear programming strategies.
Purposes
Probably the most apparent functions of the Hungarian algorithm consists of utilizing it for project issues, the place, given n duties, the objective is to optimally affiliate them with different individuals or objects (e.g., machines) that may full them.
There may be additionally a selected utility in pc imaginative and prescient. Many video monitoring algorithms (MOT) are primarily based on the mix of normal picture detection algorithms (e.g., YOLO) and logic of merging detection outcomes from a number of unbiased frames right into a video move.
Allow us to take a simplified instance of two consecutive picture frames of a video:

We run a MOT algorithm for object monitoring primarily based on YOLO. The predictions of YOLO are proven beneath in grey bins.

The target is to affiliate bounding bins between each frames to maintain observe of objects. One attainable manner to do that entails analyzing the change in distance between bounding bins between the 2 frames. It’s logical to imagine {that a} pair of bounding bins belongs to the identical object if their place don’t change rather a lot between the 2 frames.
Right here is the place the Hungarian algorithm comes into play. We are able to assemble a matrix representing pairwise distances (which would be the value features) between the coordinates of various bounding bins in each frames. We are able to discover such a mapping that minimizes the whole distance between bounding bins.

By operating the Hungarian algorithm, we get the next mappings:
(A₁, C₂), (B₁, A₂), (C₁, B₂).
We are able to confirm that they end in a complete value of 8 + 1 + 5 = 14 which is the minimal attainable operate value for this matrix. Therefore, the discovered mappings are optimum.

Actually, fashionable MOT algorithms think about extra components when matching bounding bins, together with trajectory evaluation, object velocity and path, and bodily similarity, amongst others. For simplicity, we solely thought of a single issue: the gap between the bounding bins. Nevertheless, in actuality, extra components are taken under consideration.
Conclusion
On this article, we now have appeared on the Hungarian algorithm used to resolve activity project issues. By performing easy operations on the preliminary knowledge matrix, the Hungarian algorithm transforms it to different codecs whereas sustaining the issue invariant.
Regardless of its cubic complexity, the Hungarian algorithm has a variety of functions in matching and pc imaginative and prescient issues the place the variety of objects shouldn’t be too giant.
Sources
All photos until in any other case famous are by the writer.