This text was a collaborative effort. A particular thanks to Estevão Prado, whose experience helped refine each the technical ideas and the narrative movement.
Function choice stays some of the essential but computationally costly steps within the machine studying pipeline. When working with high-dimensional datasets, figuring out which options actually contribute to predictive energy can imply the distinction between an interpretable, environment friendly mannequin and an overfit, sluggish one.
On this article, I current the Grasping Boruta algorithm—a modification to the Boruta algorithm [1] that, in our assessments, reduces computation time by 5-40× whereas mathematically provably sustaining or enhancing recall. Via theoretical evaluation and simulation experiments, I exhibit how a easy leisure of the affirmation criterion supplies assured convergence in O(-log α) iterations, the place α is the boldness stage of the binomial assessments, in comparison with the vanilla algorithm’s unbounded runtime.
The Boruta algorithm has lengthy been a favourite amongst knowledge scientists for its “all-relevant” method to function choice and its statistical framework. Not like minimal-optimal strategies, akin to Minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance (mRMR) and recursive function elimination (RFE), that search the smallest set of options for prediction, Boruta goals to establish all options that carry helpful info. This philosophical distinction issues tremendously when the aim is knowing a phenomenon somewhat than merely making predictions, as an example.
Nevertheless, Boruta’s thoroughness comes at a excessive computational value. In real-world functions with a whole lot or hundreds of options, the algorithm can take prohibitively lengthy to converge. That is the place the Grasping Boruta Algorithm enters the image.
Understanding the vanilla Boruta algorithm
Earlier than inspecting the modification, let’s recap how the vanilla Boruta algorithm works.
Boruta’s genius lies in its elegant method to figuring out function significance. Somewhat than counting on arbitrary thresholds or p-values immediately from a mannequin, it creates a aggressive benchmark utilizing shadow options.
Right here’s the method:
- Shadow function creation: For every function within the dataset, Boruta creates a “shadow” copy by randomly shuffling its values. This destroys any relationship the unique function had with the response (or goal) variable whereas preserving its distribution.
- Significance computation: A Random Forest is skilled on the mixed dataset and have importances are calculated for all options. Though Boruta was initially proposed for Random Forest estimators, the algorithm can work with some other tree-based ensemble that gives function significance scores (e.g., Extra Trees [2], XGBoost [3], LightGBM [4]).
- Hit registration: For every non-shadow function, Boruta checks whether or not the significance of the function is larger than the utmost significance of the shadows. Non-shadow options which are extra necessary than the utmost shadow are assigned a “hit” and those which are much less necessary are assigned “no-hit”.
- Statistical testing: Primarily based on the lists of hits and no-hits for every of the non-shadow options, Boruta performs a binomial take a look at to find out if its significance is considerably larger than the utmost significance amongst shadow options throughout a number of iterations.
- Resolution making: Options that constantly outperform the very best shadow function are marked as “confirmed.” Options that constantly underperform are “rejected.” Options within the center (these that aren’t statistically considerably completely different from the very best shadow) stay “tentative”.
- Iteration: Steps 2–5 repeat till all options are categorised as confirmed or rejected. On this article, I say that the Boruta algorithm “has converged” when all options are both confirmed or rejected or when a most variety of iterations has been reached.
The binomial take a look at: Boruta’s choice criterion
The vanilla Boruta makes use of a rigorous statistical framework. After a number of iterations, the algorithm performs a binomial take a look at on the hits for every of the non-shadow options:
- Null speculation: The function is not any higher than the very best shadow function (50% probability of beating shadows by random probability).
- Various speculation: The function is best than the very best shadow function.
- Affirmation criterion: If the binomial take a look at p-value is beneath α (sometimes between 0.05–0.01), the function is confirmed.
This similar course of can be carried out to reject options:
- Null speculation: The function is best than the very best shadow (50% probability of not beating shadows by random probability).
- Various speculation: The function is not any higher than the very best shadow function.
- Rejection criterion: If the binomial take a look at p-value is beneath α, the function is rejected.
This method is statistically sound and conservative; nonetheless, it requires many iterations to build up adequate proof, particularly for options which are related however solely marginally higher than noise.
The convergence downside
The vanilla Boruta algorithm faces two main convergence points:
Lengthy runtime: As a result of the binomial take a look at requires many iterations to achieve statistical significance, the algorithm may require a whole lot of iterations to categorise all options, particularly when utilizing small α values for prime confidence. Moreover, there are not any ensures or estimates for convergence, that’s, there is no such thing as a technique to decide what number of iterations might be required for all of the options to be categorized into “confirmed” or “rejected”.
Tentative options: Even after reaching a most variety of iterations, some options might stay within the “tentative” class, leaving the analyst with incomplete info.
These challenges motivated the event of the Grasping Boruta Algorithm.
The Grasping Boruta algorithm
The Grasping Boruta Algorithm introduces a basic change to the affirmation criterion that dramatically improves convergence velocity whereas sustaining excessive recall.
The title comes from the algorithm’s keen method to affirmation. Like grasping algorithms that make domestically optimum selections, Grasping Boruta instantly accepts any function that exhibits promise, with out ready to build up statistical proof. This trade-off favors velocity and sensitivity over specificity.
Relaxed affirmation
As a substitute of requiring statistical significance via a binomial take a look at, the Grasping Boruta confirms any function that has overwhelmed the utmost shadow significance not less than as soon as throughout all iterations, whereas retaining the identical rejection criterion.
The rationale behind this leisure is that in “all-relevant” function choice, because the title suggests, we sometimes prioritize retaining all related options over eliminating all irrelevant options. The additional elimination of the non-relevant options could be carried out with “minimal-optimal” function choice algorithms downstream within the machine studying pipeline. Due to this fact, this leisure is virtually sound and produces the anticipated outcomes from an “all-relevant” function choice algorithm.
This seemingly easy change has a number of necessary implications:
- Maintained recall: As a result of we’re stress-free the affirmation criterion (making it simpler to substantiate options), we are able to by no means have decrease recall than the vanilla Boruta. Any function that’s confirmed by the vanilla technique can even be confirmed by the grasping model. This may be simply confirmed since it’s inconceivable for a function to be deemed extra necessary than the very best shadow within the binomial take a look at with no single hit.
- Assured Convergence in Ok iterations: As might be proven beneath, this variation makes it in order that it’s potential to compute what number of iterations are required till all options are both confirmed or rejected.
- Sooner convergence: As a direct consequence of the purpose above, the Grasping Boruta algorithm wants far much less iterations than the vanilla Boruta for all options to be sorted. Extra particularly, the minimal variety of iterations for the vanilla algorithm to type its “first batch” of options is identical at which the grasping model finishes operating.
- Hyperparameter Simplification: One other consequence of the assured convergence is that a number of the parameters used within the vanilla Boruta algorithm, akin to max_iter (most variety of iterations), early_stopping (boolean figuring out whether or not the algorithm ought to cease earlier if no change is seen throughout quite a few iterations) and n_iter_no_change (minimal variety of iterations with no change earlier than early stopping is triggered), could be totally eliminated with out loss in flexibility. This simplification improves the algorithm’s usability and makes the function choice course of simpler to handle.
The modified algorithm
The Grasping Boruta algorithm follows this course of:
- Shadow function creation: Precisely the identical because the vanilla Boruta. Shadow options are created based mostly on every of the options of the dataset.
- Significance computation: Precisely the identical because the vanilla Boruta. Function significance scores are computed based mostly on any tree-based ensemble machine studying algorithm.
- Hit registration: Precisely the identical because the vanilla Boruta. Assigns hits to non-shadow options which are extra necessary than an important shadow function.
- Statistical testing: Primarily based on the lists of no-hits for every of the non-shadow function, Grasping Boruta performs a binomial take a look at to find out whether or not its significance is just not considerably larger than the utmost significance amongst shadow options throughout a number of iterations.
- Resolution making [Modified]: Options with not less than one hit are confirmed. Options that constantly underperform in relation to the very best shadow are “rejected.” Options with zero hits stay “tentative”.
- Iteration: Steps 2–5 repeat till all options are categorised as confirmed or rejected.
This grasping model relies on the unique boruta_py [5] implementation with a couple of tweaks, so most issues are stored the identical as this implementation, aside from the adjustments talked about above.
Statistical perception on convergence assure
Probably the most elegant properties of the Grasping Boruta Algorithm is its assured convergence inside a specified variety of iterations that will depend on the chosen α worth.
Due to the relaxed affirmation criterion, we all know that any function with a number of hits is confirmed and we don’t have to run binomial assessments for affirmation. Conversely, we all know that each tentative function has zero hits. This reality drastically simplifies the equation representing the binomial take a look at required to reject options.
Extra particularly, the binomial take a look at is simplified as follows. Contemplating the one-sided binomial take a look at described above for rejection within the vanilla Boruta algorithm, with H₀ being p = p₀ and H₁ being p < p₀, the p-value is calculated as:
This system sums the possibilities of observing ok successes for all values from ok = 0 as much as the noticed x. Now, given the identified values on this state of affairs (p₀ = 0.5 and x = 0), the system simplifies to:

To reject H₀ at significance stage α, we want:

Substituting our simplified p-value:

Taking the reciprocal (and reversing the inequality):

Taking logarithms base 2 of either side:

Due to this fact, the pattern dimension required is:

This suggests that at most ⌈ log₂(1/α)⌉ iterations of the Grasping Boruta algorithm are run till all options are sorted into both “confirmed” or “rejected” and convergence has been achieved. Which means that the Grasping Boruta algorithm has O(-log α) complexity.
One other consequence of all tentative options having 0 hits is the truth that we are able to additional optimize the algorithm by not operating any statistical assessments throughout iterations.
Extra particularly, given α, it’s potential to find out the utmost variety of iterations Ok required to reject a variable. Due to this fact, for each iteration < Ok, if a variable has successful, it’s confirmed, and if it doesn’t, it’s tentative (for the reason that p-value for all iterations < Ok might be larger than α). Then, at precisely iteration Ok, all variables which have 0 hits could be moved into the rejected class with no binomial assessments being run, since we all know that the p-values will all be smaller than α at this level.
This additionally implies that, for a given α, the full variety of iterations run by the Grasping Boruta algorithm is the same as the minimal variety of iterations it takes for the vanilla implementation to both verify or reject any function!
Lastly, you will need to notice that the boruta_py implementation makes use of False Discovery Charge (FDR) correction to account for the elevated probability of false positives when performing a number of speculation assessments. In follow, the required worth of Ok is just not precisely as proven within the equation above, however the complexity in relation to α remains to be logarithmic.
The desk beneath accommodates the variety of required iterations for various α values with the correction utilized:

Simulation experiments
To empirically consider the Grasping Boruta Algorithm, I performed experiments utilizing artificial datasets the place the bottom fact is thought. This method permits exact measurement of the algorithm’s efficiency.
Methodology
Artificial knowledge technology: I created datasets with a identified set of necessary and unimportant options utilizing sklearn’s make_classification operate, permitting for direct computation of choice efficiency metrics. Moreover, these datasets embrace ‘redundant options’—linear mixtures of informative options that carry predictive info however usually are not strictly vital for prediction. Within the ‘all-relevant’ paradigm, these options ought to ideally be recognized as necessary since they do comprise sign, even when that sign is redundant. The analysis due to this fact considers informative options and redundant options collectively because the ‘floor fact related set’ when computing recall.
Metrics: Each algorithms are evaluated on:
- Recall (Sensitivity): What quantity of actually necessary options had been accurately recognized?
- Specificity: What quantity of actually unimportant options had been accurately rejected?
- F1 Rating: The harmonic imply of precision and recall, balancing the trade-off between accurately figuring out necessary options and avoiding false positives
- Computational time: Wall-clock time to completion
Experiment 1 – Various α
Dataset traits
X_orig, y_orig = sklearn.make_classification(
n_samples=1000,
n_features=500,
n_informative=5,
n_redundant=50, # LOTS of redundant options correlated with informative
n_repeated=0,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
flip_y=0.3, # Some label noise
class_sep=0.0001,
random_state=42
)This constitutes a “arduous” function choice downside due to the excessive dimensionality (500 variables), with a small pattern dimension (1000 samples), small variety of related options (sparse downside, with round 10% of the options being related in any approach) and pretty excessive label noise. You will need to create such a “arduous” downside to successfully evaluate the performances of the strategies, in any other case, each strategies obtain near-perfect outcomes after just a few iterations.
Hyperparameters used
On this experiment, we assess how the algorithms carry out with completely different α, so we evaluated each strategies utilizing α from the record [0.00001, 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 0.2].
Relating to the hyperparameters of the Boruta and Grasping Boruta algorithms, each use an sklearn ExtraTreesClassifier because the estimator with the next parameters:
ExtraTreesClassifier(
n_estimators: 500,
max_depth: 5,
n_jobs: -1,
max_features: 'log2'
)The Further Bushes classifier was chosen because the estimator due to its quick becoming time and the truth that it’s extra steady when contemplating function significance estimation duties [2].
Lastly, the vanilla Boruta makes use of no early stopping (this parameter is not sensible within the context of Grasping Boruta).
Variety of trials
The vanilla Boruta algorithm is configured to run at most 512 iterations however with a early stopping situation. Which means that if no adjustments are seen in X iterations (n_iter_no_change), the run stops. For every α, a price of n_iter_no_change is outlined as follows:

Early stopping is enabled as a result of a cautious person of the vanilla Boruta algorithm would set this if the wall-clock time of the algorithm run is high-enough, and is a extra wise use of the algorithm general.
These early stopping thresholds had been chosen to steadiness computational value with convergence probability: smaller thresholds for bigger α values (the place convergence is quicker) and bigger thresholds for smaller α values (the place statistical significance takes extra iterations to build up). This displays how a sensible person would configure the algorithm to keep away from unnecessarily lengthy runtimes.
Outcomes: efficiency comparability

Key discovering: As offered within the left-most panel of determine 1, Grasping Boruta achieves recall that’s larger than or equal to that of the vanilla Boruta throughout all experimental situations. For the 2 smallest α values, the recall is equal and for the others, the Grasping Boruta implementation has barely larger recall, confirming that the relaxed affirmation criterion doesn’t miss options that the vanilla technique would catch.
Noticed trade-off: Grasping Boruta exhibits modestly decrease specificity in some settings, confirming that the relaxed criterion does end in extra false positives. Nevertheless, the magnitude of this impact is smaller than anticipated, leading to solely 2-6 extra options being chosen on this dataset with 500 variables. This elevated false-positive charge is appropriate in most downstream pipelines for 2 causes: (1) absolutely the variety of extra options is small (2-6 options on this 500-feature dataset), and (2) subsequent modeling steps (e.g., regularization, cross-validation, or minimal-optimal function choice) can filter these options if they don’t contribute to predictive efficiency.
Speedup: Grasping Boruta constantly requires 5-15× much less time when in comparison with the vanilla implementation, with the speedup rising for extra conservative α values. For α = 0.00001, the advance approaches 15x. It’s also anticipated that even smaller α values would result in more and more bigger speedups. You will need to notice that for many situations with α < 0.001, the vanilla Boruta implementation “doesn’t converge” (not all options are confirmed or rejected) and with out early-stopping, they’d run for for much longer than this.
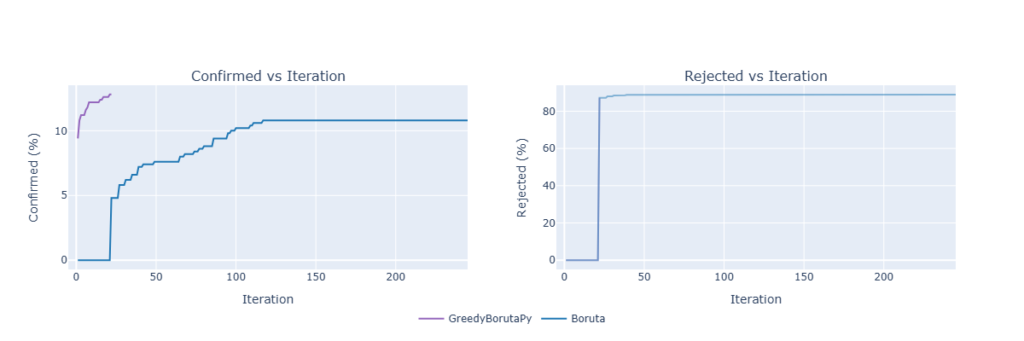
Convergence: We will additionally consider how briskly every of the strategy “converges” by analysing the standing of the variables at every iteration, as proven within the plot beneath:

On this state of affairs, utilizing α = 0.00001, we are able to observe the conduct talked about above: the primary affirmation/rejection of the vanilla algorithm happens on the final iteration of the grasping algorithm (therefore the entire overlap of the strains within the rejection plot).
Due to the logarithmic progress of the utmost variety of iterations by the Grasping Boruta by way of α, we are able to additionally discover excessive values for α when utilizing the grasping model:

Experiment 2 – Exploring most variety of iterations
Parameters
On this experiment, the identical dataset and hyperparameters as described within the final experiment had been used, aside from α which was fastened at α = 0.00001, and the utmost variety of iterations (for the vanilla algorithm) modified throughout runs. The utmost numbers of iterations analyzed are [16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512]. Additionally, early stopping was disabled for this experiment to be able to showcase one of many weaknesses of the vanilla Boruta algorithm.
You will need to notice that for this experiment there is just one knowledge level for the Grasping Boruta technique for the reason that most variety of iterations is just not a parameter by itself on the modified model, since it’s uniquely outlined by the α used.
Outcomes: Efficiency Comparability

As soon as once more, we observe that the Grasping Boruta achieves greater recall than the vanilla Boruta algorithm whereas having barely decreased specificity, throughout all of the variety of iterations thought-about. On this state of affairs, we additionally observe that the Grasping Boruta achieves recall ranges much like these of the vanilla algorithm in ~4x much less time.
Moreover, as a result of within the vanilla algorithm there is no such thing as a “assure of convergence” in a given variety of iterations, the person should outline a most variety of iterations for which the algorithm will run. In follow, it’s troublesome to find out this quantity with out realizing the bottom fact for necessary options and the potential accompanying variety of iterations to set off early stopping. Contemplating this issue, an excessively conservative person might run the algorithm for a lot too many iterations with no vital enchancment within the function choice high quality.
On this particular case, utilizing a most variety of iterations equal to 512 iterations, with out early stopping, achieves a recall similar to that achieved with 64, 128 and 256 iterations. When evaluating the grasping model to the 512 iterations of the vanilla algorithm, we see {that a} 40x speedup is achieved, whereas having a barely larger recall.
When to make use of Grasping Boruta?
The Grasping Boruta Algorithm is especially helpful in particular situations:
- Excessive-dimensional knowledge with restricted time: When working with datasets that comprise a whole lot or hundreds of options, the computational value of the vanilla Boruta could be prohibitive. If fast outcomes are required for exploratory evaluation or speedy prototyping, Grasping Boruta gives a compelling speed-accuracy trade-off.
- All-relevant function choice targets: In case your goal aligns with Boruta’s authentic “all-relevant” philosophy—discovering each function that contributes with some info somewhat than the minimal optimum set—then Grasping Boruta’s excessive recall is precisely what you want. The algorithm favors inclusion, which is acceptable when function elimination is expensive (e.g., in scientific discovery or causal inference duties).
- Iterative evaluation workflows: In follow, function choice isn’t a one-shot choice. Knowledge scientists usually iterate, experimenting with completely different function units and fashions. Grasping Boruta permits speedy iteration by offering quick preliminary outcomes that may be refined in subsequent analyses. Moreover, different function choice strategies can be utilized to additional cut back the dimensionality of the function set.
- A number of additional options are OK: The vanilla Boruta’s strict statistical testing is efficacious when false positives are significantly expensive. Nevertheless, in lots of functions, together with a couple of additional options is preferable to lacking necessary ones. Grasping Boruta is good when the downstream pipeline can deal with barely bigger function units however advantages from sooner processing.
Conclusion
The Grasping Boruta algorithm is an extension/modification to a well-established function choice technique, with considerably completely different properties. By stress-free the affirmation criterion from statistical significance to a single hit, we obtain:
- 5-40x sooner run instances in comparison with commonplace Boruta, for the situations explored.
- Equal or larger recall, making certain no related options are missed.
- Assured convergence with all options categorised.
- Maintained interpretability and theoretical grounding.
The trade-off—a modest improve within the false constructive charge—is appropriate in lots of real-world functions, significantly when working with high-dimensional knowledge below time constraints.
For practitioners, the Grasping Boruta algorithm gives a helpful instrument for speedy, high-recall function choice in exploratory evaluation, with the choice to comply with up with extra conservative strategies if wanted. For researchers, it demonstrates how considerate modifications to established algorithms can yield vital sensible advantages by rigorously contemplating the precise necessities of real-world functions.
The algorithm is most applicable when your philosophy aligns with discovering “all related” options somewhat than a minimal set, when velocity issues, and when false positives could be tolerated or filtered in downstream evaluation. In these frequent situations, Grasping Boruta supplies a compelling different to the vanilla algorithm.
References
[1] Kursa, M. B., & Rudnicki, W. R. (2010). Function Choice with the Boruta Package deal. Journal of Statistical Software program, 36(11), 1–13.
[2] Geurts, P., Ernst, D., & Wehenkel, L. (2006). Extraordinarily randomized bushes. Machine Studying, 63(1), 3–42.
[3] Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. Proceedings of the twenty second ACM SIGKDD Worldwide Convention on Data Discovery and Knowledge Mining, 785–794.
[4] Ke, G., Meng, Q., Finley, T., Wang, T., Chen, W., Ma, W., Ye, Q., & Liu, T.-Y. (2017). LightGBM: A extremely environment friendly gradient boosting choice tree. Advances in Neural Data Processing Programs 30 (NIPS 2017), 3146–3154.
[5] BorutaPy implementation: https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib/boruta_py
Code availability
The whole implementation of Grasping Boruta is accessible at GreedyBorutaPy.
Grasping Boruta can be obtainable as a PyPI bundle at greedyboruta.
Thanks for studying! Should you discovered this text useful, please take into account following for extra content material on function choice, machine studying algorithms, and sensible knowledge science.