The trade’s outliers have distorted our definition of Recommender Programs. TikTok, Spotify, and Netflix make use of hybrid deep studying fashions combining collaborative- and content-based filtering to ship customized suggestions you didn’t even know you’d like. For those who’re contemplating a RecSys function, you would possibly count on to dive into these immediately. However not all RecSys issues function — or have to function — at this degree. Most practitioners work with comparatively easy, tabular fashions, typically gradient-boosted bushes. Till attending RecSys ’25 in Prague, I assumed my expertise was an outlier. Now I imagine that is the norm, hidden behind the large outliers that drive the trade’s cutting-edge. So what units these giants aside from most different firms? On this article, I take advantage of the framework mapped within the picture above to motive about these variations and assist place your personal suggestion work on the spectrum.
Most suggestion techniques start with a candidate era part, decreasing thousands and thousands of attainable gadgets to a manageable set that may be re-ranked by higher-latency options. However candidate era isn’t at all times the uphill battle it’s made out to be, nor does it essentially require machine studying. Contexts with well-defined scopes and onerous filters typically don’t require advanced querying logic or vector search. Take into account Reserving.com: when a person searches for “4-star motels in Barcelona, September 12-15,” the geography and availability constraints have already narrowed thousands and thousands of properties down to some hundred—even when the backend techniques dealing with that filtering are themselves advanced. The actual problem for machine studying practitioners is then rating these motels with precision. That is vastly totally different from Amazon’s product search or the YouTube homepage, the place onerous filters are absent. In these environments, the system should depend on semantic intent or previous conduct to floor related candidates from thousands and thousands or billions of things earlier than re-ranking even takes place.
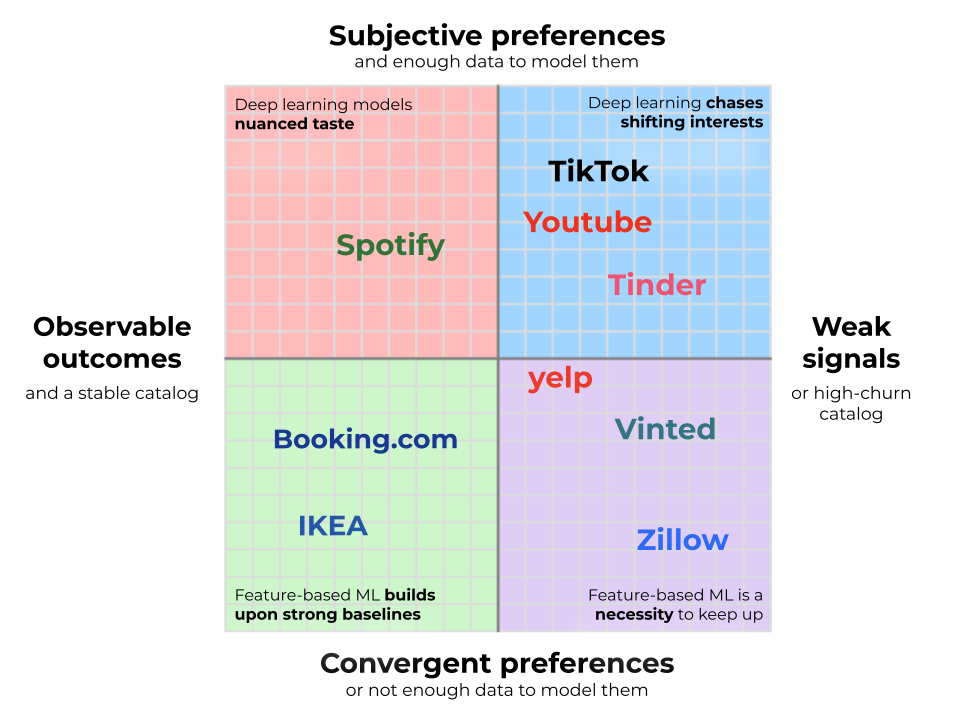
Past candidate era, the complexity of re-ranking is finest understood by way of the 2 dimensions mapped within the picture under. First, observable outcomes and catalog stability, which determines how robust a baseline you’ll be able to have. Second, the subjectivity of preferences and their learnability, which determines how advanced your personalization answer needs to be.
Observable Outcomes and Catalog Stability
On the left finish of the x-axis are companies that immediately observe their most necessary outcomes. Giant retailers like IKEA are a great instance of this: when a buyer buys an ESKILSTUNA couch as a substitute of a KIVIK, the sign is unambiguous. Combination sufficient of those, and the corporate is aware of precisely which product has the upper buy fee. When you’ll be able to immediately observe customers voting with their wallets, you’ve got a robust baseline that’s onerous to beat.
On the different excessive are platforms that may’t observe whether or not their suggestions really succeeded. Tinder and Bumble would possibly see customers match, however they typically received’t know whether or not the pair hit it off (particularly as customers transfer off to different platforms). Yelp and Google Maps can advocate eating places, however for the overwhelming majority, they’ll’t observe whether or not you really visited, simply which listings you clicked. Counting on such upper-funnel indicators means place bias dominates: gadgets in high positions accumulate interactions no matter true high quality, making it almost unattainable to inform whether or not engagement displays real choice or mere visibility. Distinction this with the IKEA instance: a person would possibly click on a restaurant on Yelp just because it appeared first, however they’re far much less possible to purchase a settee for that very same motive. Within the absence of a tough conversion, you lose the anchor of a dependable leaderboard. This forces you to work a lot tougher to extract sign from the noise. Opinions can supply some grounding, however they’re hardly ever dense sufficient to work as a main sign. As an alternative, you might be left to run countless experiments in your rating heuristics, continually tuning logic to squeeze a proxy for high quality out of a stream of weak indicators.
Excessive-Churn Catalog
Even with observable outcomes, nevertheless, a robust baseline just isn’t assured. In case your catalog is continually altering, it’s possible you’ll not accumulate sufficient information to construct a correct leaderboard. Actual property platforms like Zillow and secondhand websites like Vinted face probably the most excessive model: every merchandise has a listing of 1, disappearing the second it’s bought. This forces you to depend on simplistic and inflexible kinds like “latest first” or “lowest value per sq. meter.” These are far weaker than conversion leaderboards based mostly on actual, dense person sign. To do higher, you could leverage machine studying to foretell conversion likelihood instantly, combining intrinsic attributes with debiased short-term efficiency to floor the perfect stock earlier than it disappears.
The Ubiquity of Characteristic-Primarily based Fashions
No matter your catalog’s stability or sign energy, the core problem stays the identical: you are attempting to enhance upon no matter baseline is accessible. That is usually achieved by coaching a machine studying (ML) mannequin to foretell the likelihood of engagement or conversion given a selected context. Gradient-boosted bushes (GBDTs) are the pragmatic alternative, a lot sooner to coach and tune than deep studying.
GBDTs predict these outcomes based mostly on engineered merchandise options: categorical and numerical attributes that quantify and describe a product. Even earlier than particular person preferences are recognized, GBDTs also can adapt suggestions leveraging fundamental person options like nation and machine sort. With these merchandise and person options alone, an ML mannequin can already enhance upon the baseline — whether or not meaning debiasing a reputation leaderboard or rating a high-churn feed. As an illustration, in style e-commerce, fashions generally use location and time of yr to floor gadgets tied to the season, whereas concurrently utilizing nation and machine to calibrate the worth level.
These options enable the mannequin to fight the aforementioned place bias by separating true high quality from mere visibility. By studying which intrinsic attributes drive conversion, the mannequin can appropriate for the place bias inherent in your reputation baseline. It learns to determine gadgets that carry out on advantage, slightly than just because they have been ranked on the high. That is tougher than it seems to be: you danger demoting confirmed winners greater than it’s best to, doubtlessly degrading the expertise.
Opposite to standard perception, feature-based fashions also can drive personalization, relying on how a lot semantic data gadgets naturally include. Platforms like Reserving.com and Yelp accumulate wealthy descriptions, a number of images, and person critiques that present semantic depth per itemizing. These could be encoded into semantic embeddings for personalization: through the use of the person’s current interactions, we are able to calculate similarity scores in opposition to candidate gadgets and feed these to the gradient-boosted mannequin as options.
This strategy has its limits, nevertheless. Characteristic-based fashions can advocate based mostly on similarity to current interactions, however not like collaborative filtering, they don’t immediately study which gadgets are typically favored by comparable customers. To study that, they want merchandise similarity scores supplied as enter options. Whether or not this limitation issues relies on one thing extra basic: how a lot customers really disagree.
Subjectivity
Not all domains are equally private or controversial. In some, customers largely agree on what makes a great product as soon as fundamental constraints are glad. We name these convergent preferences, and so they occupy the underside half of the chart. Take Reserving.com: vacationers could have totally different budgets and site preferences, however as soon as these are revealed by way of filters and map interactions, rating standards converge — greater costs are dangerous, facilities are good, good critiques are higher. Or think about Staples: as soon as a person wants printer paper or AA batteries, model and value dominate, making person preferences remarkably constant.
On the different excessive — the highest half — are subjective domains outlined by extremely fragmented style. Spotify exemplifies this: one person’s favourite monitor is one other’s rapid skip. But, style hardly ever exists in a vacuum. Someplace within the information is a person in your actual wavelength, and machine studying bridges the hole, turning their discoveries from yesterday into your suggestions for at this time. Right here, the worth of personalization is big, and so is the technical funding required.
The Proper Knowledge
Subjective style is barely actionable in case you have sufficient information to look at it. Many domains contain distinct preferences however lack the suggestions loop to seize them. A distinct segment content material platform, new market, or B2B product could face wildly divergent tastes but lack the clear sign to study them. Yelp restaurant suggestions illustrate this problem: eating preferences are subjective, however the platform can’t observe precise restaurant visits, solely clicks. This implies they’ll’t optimize personalization for the true goal (conversions). They’ll solely optimize for proxy metrics like clicks, however extra clicks would possibly really sign failure, indicating customers are shopping a number of listings with out discovering what they need.
However in subjective domains with dense behavioral information, failing to personalize leaves cash on the desk. YouTube exemplifies this: with billions of day by day interactions, the platform learns nuanced viewer preferences and surfaces movies you didn’t know you wished. Right here, deep studying turns into unavoidable. That is the purpose the place you’ll see giant groups coordinating over Jira and cloud payments that require VP approval. Whether or not that complexity is justified comes down solely to the info you’ve got.
Know The place You Stand
Understanding the place your drawback sits on this spectrum is much extra precious than blindly chasing the most recent structure. The trade’s “state-of-the-art” is essentially outlined by the outliers — the tech giants coping with large, subjective inventories and dense person information. Their options are well-known as a result of their issues are excessive, not as a result of they’re universally appropriate.
Nonetheless, you’ll possible face totally different constraints in your personal work. In case your area is outlined by a steady catalog and observable outcomes, you land within the bottom-left quadrant alongside firms like IKEA and Reserving.com. Right here, reputation baselines are so robust that the problem is solely constructing upon them with machine studying fashions that may drive measurable A/B take a look at wins. If, as a substitute, you face excessive churn (like Vinted) or weak indicators (like Yelp), machine studying turns into a necessity simply to maintain up.
However that doesn’t imply you’ll want deep studying. That added complexity solely really pays off in territories the place preferences are deeply subjective and there’s sufficient information to mannequin them. We frequently deal with techniques like Netflix or Spotify because the gold customary, however they’re specialised options to uncommon circumstances. For the remainder of us, excellence isn’t about deploying probably the most advanced structure obtainable; it’s about recognizing the constraints of the terrain and having the boldness to decide on the answer that solves your issues.
Photos by the writer.