within the federated studying sequence I’m doing, and should you simply landed right here, I might advocate going by way of the first part the place we mentioned how federated studying works at a excessive stage. For a fast refresher, right here is an interactive app that I created in a marimo pocket book the place you possibly can carry out native coaching, merge fashions utilizing the Federated Averaging (FedAvg) algorithm and observe how the worldwide mannequin improves throughout federated rounds.
On this half, our focus might be on implementing the federated logic utilizing the Flower framework.
What occurs when fashions are skilled on skewed datasets
Within the first half, we mentioned how federated studying was used for early COVID screening with Curial AI. If the mannequin had been skilled solely on knowledge from a single hospital, it could have learnt patterns particular to that hospital solely and would have generalised badly on out-of-distribution datasets. We all know it is a concept, however now allow us to put a quantity to it.
I’m borrowing an instance from the Flower Labs course on DeepLearning.AI as a result of it makes use of the acquainted which makes the thought simpler to know with out getting misplaced in particulars. This instance makes it simple to know what occurs when fashions are skilled on biased native datasets. We then use the identical setup to point out how federated studying modifications the end result.
- I’ve made a number of small modifications to the unique code. Specifically, I take advantage of the Flower Datasets library, which makes it simple to work with datasets for federated studying situations.
- 💻 You’ll be able to entry the code right here to observe alongside.
Splitting the Dataset
We begin by taking the MNIST dataset and splitting it into three components to signify knowledge held by completely different shoppers, let’s say three completely different hospitals. Moreover, we take away sure digits from every break up so that each one shoppers have incomplete knowledge, as proven beneath. That is completed to simulate real-world knowledge silos.

As proven within the picture above, shopper 1 by no means sees digits 1, 3 and seven. Equally, shopper 2 by no means sees 2, 5 and eight and shopper 3 by no means sees 4, 6, and 9. Though all three datasets come from the identical supply, they signify fairly completely different distributions.
Coaching on Biased Knowledge
Subsequent, we practice separate fashions on every dataset utilizing the identical structure and coaching setup. We use a quite simple neural community carried out in PyTorch with simply two totally linked layers and practice the mannequin for 10 epochs.

As might be seen from the loss curves above, the loss regularly goes down throughout coaching. This means that the fashions are studying one thing. Nonetheless, bear in mind, every mannequin is barely studying from its personal restricted view of the information and it’s solely once we check it on a held-out set that we’ll know the true accuracy.
Evaluating on Unseen Knowledge
To check the fashions, we load the MNIST check dataset with the identical normalization utilized to the coaching knowledge. Once we consider these fashions on the whole check set (all 10 digits), accuracy lands round 65 to 70 %, which appears affordable provided that three digits had been lacking from every coaching dataset. At the very least the accuracy is healthier than the random likelihood of 10%.
Subsequent, we additionally consider how particular person fashions carry out on knowledge examples that weren’t represented of their coaching set. For that, we create three particular check subsets:
- Take a look at set [1,3,7] solely contains digits 1, 3, and seven
- Take a look at set [2,5,8] solely contains digits 2, 5, and eight
- Take a look at set [4,6,9] solely contains digits 4, 6, and 9

Once we consider every mannequin solely on the digits it by no means noticed throughout coaching, accuracy drops to 0 %. The fashions utterly fail on courses they had been by no means uncovered to. Nicely, that is additionally anticipated since a mannequin can’t study to acknowledge patterns it has by no means seen earlier than. However there’s greater than what meets the attention, so we subsequent have a look at the confusion matrix to know the conduct in additional element.
Understanding the Failure Via Confusion Matrices
Under is the confusion matrix for mannequin 1 that was skilled on knowledge excluding digits 1, 3, and seven. Since these digits had been by no means seen throughout coaching, the mannequin nearly by no means predicts these labels.
Nonetheless, In few instances, the mannequin predicts visually related digits as a substitute. When label 1 is lacking, the mannequin by no means outputs 1 and as a substitute predicts digits like 2 or 8. The identical sample seems for different lacking courses. Which means that the mannequin fails in a manner by assigning excessive confidence to the flawed label. That is undoubtedly not anticipated.

This instance reveals the boundaries of centralized coaching with skewed knowledge. When every shopper has solely a partial view of the true distribution, fashions fail in systematic ways in which general accuracy doesn’t seize. That is precisely the issue federated studying is supposed to handle and that’s what we are going to implement within the subsequent part utilizing the Flower framework.
What’s Flower 🌼 ?
Flower is an open supply framework that makes federated studying very simple to implement, even for inexperienced persons. It’s framework agnostic so that you don’t have to fret about utilizing PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face, JAX and extra. Additionally, the identical core abstractions apply whether or not you’re working experiments on a single machine or coaching throughout actual gadgets in manufacturing.
Flower fashions federated studying in a really direct manner. A Flower app is constructed across the identical roles we mentioned within the earlier article: shoppers, a server and a method that connects them. Let’s now have a look at these roles in additional element.
Understanding Flower Via Simulation
Flower makes it very simple to start out with federated studying with out worrying about any complicated setup. For native simulation, there are mainly two instructions you have to care about:
- one to generate the app —
flwr newand - one to run it—
flwr run
You outline a Flower app as soon as after which run it regionally to simulate many consumers. Though all the things runs on a single machine, Flower treats every shopper as an impartial participant with its personal knowledge and coaching loop. This makes it a lot simpler to experiment and check earlier than transferring to an actual deployment.
Allow us to begin by putting in the newest model of Flower, which on the time of writing this text is 1.25.0.
# Set up flower in a digital setting
pip set up -U flwr
# Checking the put in model
flwr --version
Flower model: 1.25.0The quickest strategy to create a working Flower app is to let Flower scaffold one for you by way of flwr new.
flwr new #to pick from an inventory of templates
or
flwr new @flwrlabs/quickstart-pytorch #straight specify a templateYou now have a whole mission with a clear construction to start out with.
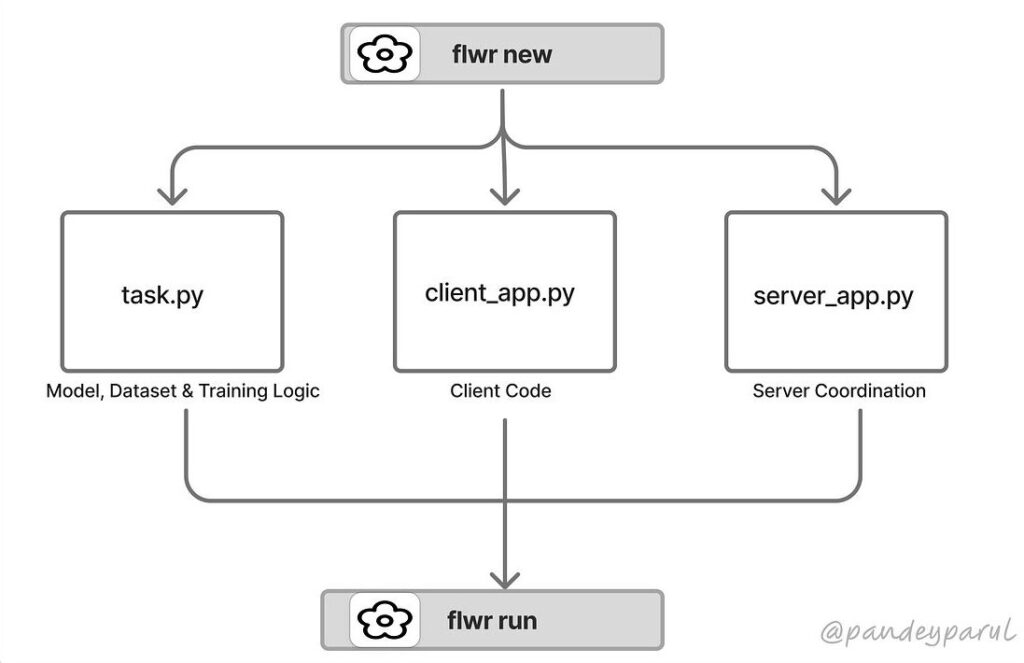
quickstart-pytorch
├── pytorchexample
│ ├── client_app.py
│ ├── server_app.py
│ └── activity.py
├── pyproject.toml
└── README.mdThere are three most important information within the mission:
- The
activity.pyfile defines the mannequin, dataset and coaching logic. - The
client_app.pyfile defines what every shopper does regionally. - The
server_app.pyfile coordinates coaching and aggregation, often utilizing federated averaging however you may as well modify it.
Operating the federated simulation
We are able to now run the federation utilizing the instructions beneath.
pip set up -e .
flwr run .This single command begins the server, creates simulated shoppers, assigns knowledge partitions and runs federated coaching finish to finish.

An vital level to notice right here is that the server and shoppers don’t name one another straight. All communication occurs utilizing message objects. Every message carries mannequin parameters, metrics, and configuration values. Mannequin weights are despatched utilizing array data, metrics similar to loss or accuracy are despatched utilizing metric data and values like studying price are despatched utilizing config data. Throughout every spherical, the server sends the present international mannequin to chose shoppers, shoppers practice regionally and return up to date weights with metrics and the server aggregates the outcomes. The server may run an analysis step the place shoppers solely report metrics, with out updating the mannequin.
In the event you look contained in the generated pyproject.toml, additionally, you will see how the simulation is outlined.
[tool.flwr.app.components]
serverapp = "pytorchexample.server_app:app"
clientapp = "pytorchexample.client_app:app"This part tells Flower which Python objects implement the ServerApp and ClientApp. These are the entry factors Flower makes use of when it launches the federation.
[tool.flwr.app.config]
num-server-rounds = 3
fraction-evaluate = 0.5
local-epochs = 1
learning-rate = 0.1
batch-size = 32
[tool.flwr.federations]
default = "local-simulation"
[tool.flwr.federations.local-simulation]
choices.num-supernodes = 10Subsequent, these values outline the run configuration. They management what number of server rounds are executed, how lengthy every shopper trains regionally and which coaching parameters are used. These settings can be found at runtime by way of the Flower Context object.
[tool.flwr.federations]
default = "local-simulation"
[tool.flwr.federations.local-simulation]
choices.num-supernodes = 10This part defines the native simulation itself. Setting choices.num-supernodes = 10 tells Flower to create ten simulated shoppers. Every SuperNode runs one ClientApp occasion with its personal knowledge partition.
Here’s a fast rundown of the steps talked about above.

Now that we’ve got seen how simple it’s to run a federated simulation with Flower, we are going to apply this construction to our MNIST instance and revisit the skewed knowledge downside we noticed earlier.
Enhancing Accuracy by way of Collaborative Coaching
Now let’s return to our MNIST instance. We noticed that the fashions skilled on particular person native datasets didn’t give good outcomes. On this part, we alter the setup in order that shoppers now collaborate by sharing mannequin updates as a substitute of working in isolation. Every dataset, nevertheless, continues to be lacking sure digits like earlier than and every shopper nonetheless trains regionally.
One of the best half concerning the mission obtained by way of simulation within the earlier part is that it could actually now be simply tailored to our use case. I’ve taken the flower app generated in the previous section and made a number of modifications within the client_app ,server_app and the activity file. I configured the coaching to run for 3 server rounds, with all shoppers collaborating in each spherical, and every shopper coaching its native mannequin for ten native epochs. All these settings might be simply managed by way of the pyproject.toml file. The native fashions are then aggregated to a single international mannequin utilizing Federated Averaging.


Now let’s have a look at the outcomes. Keep in mind that within the remoted coaching strategy, the three particular person fashions achieved an accuracy of roughly between 65 and 70%. Right here, with federated studying, we see an enormous bounce in accuracy to round 96%. Which means that the worldwide mannequin is significantly better than any of the person fashions skilled in isolation.
This international mannequin even performs higher on the particular subsets (the digits that had been lacking from every shopper’s knowledge) and sees a bounce in accuracy from beforehand 0% to between 94 and 97%.

The confusion matrix above corroborates this discovering. It reveals the mannequin learns the best way to classify all digits correctly, even those to which it was not uncovered. We don’t see any columns that solely have zeros in them anymore and each digit class now has predictions, exhibiting that collaborative coaching enabled the mannequin to study the whole knowledge distribution with none single shopper gaining access to all digit sorts.
Wanting on the large image
Whereas it is a toy instance, it helps to offer the instinct behind why federated studying is so highly effective. This identical precept might be utilized to conditions the place knowledge is distributed throughout a number of places and can’t be centralized resulting from privateness or regulatory constraints.

For example, should you substitute the above instance with, let’s say, three hospitals, every having native knowledge, you’d see that despite the fact that every hospital solely has its personal restricted dataset, the general mannequin skilled by way of federated studying can be significantly better than any particular person mannequin skilled in isolation. Moreover, the information stays non-public and safe in every hospital however the mannequin advantages from the collective data of all collaborating establishments.
Conclusion & What’s Subsequent
That’s all for this a part of the sequence. On this article, we carried out an end-to-end Federated Studying loop with Flower, understood the varied parts of the Flower app and in contrast machine studying with and with out collaborative studying. Within the subsequent half, we are going to discover Federated Studying from the privateness viewpoint. Whereas federated studying itself is a knowledge minimization answer because it prevents direct entry to knowledge, the mannequin updates exchanged between shopper and server can nonetheless doubtlessly result in privateness leaks. Let’s contact upon this within the subsequent half. For now, it’ll be an excellent concept to look into the official documentation.