is having an id disaster.
Indications of this disaster have been round for years. As an example, the inaugural subject of Harvard Information Science Evaluation discovered it simpler to outline what information science will not be relatively than what it’s (Meng, 2019). This confusion hasn’t cleared up. Actually, a case will be made that it has gotten worse. As Meng famous years in the past (2019), most of us have some data about different kinds of scientists. However what’s an information scientist and what precisely do they do?
The historical past of knowledge science is deeply rooted in statistics. Way back to 1962, one of the influential statisticians of the twentieth century, John Tukey, was calling for recognition of a brand new science targeted on studying from information. Subsequent work by the statistics neighborhood, significantly Jeff Wu (Donoho, 2015) and William Cleveland (2001), formally proposed the title “information science” and urged educational statistics increase its boundaries (Donoho, 2015). But, the following years have seen a big affect from laptop science, requires information science to be acknowledged as a novel self-discipline distinct from statistics, and a basic reckoning with information science being a science.
The enlargement of the probabilistic and inferential traditions of statistics together with the algorithmic, programming, and system-design issues of laptop science has led to a contemporary view of knowledge science as an interdisciplinary subject, which Blei and Smyth (2017) affectionately confer with as ‘the kid of statistics and laptop science’. Wing and colleagues (2018) see the defining attribute being information science isn’t just about strategies, but additionally about using these strategies within the context of a site. This interaction between area and strategies makes information science not merely the sum of its components, however a definite subject with its personal focus.
But, there’s the elemental query of the title itself. Wing’s probing query (2020), “Is there an issue distinctive to information science that one can convincingly argue wouldn’t be addressed or requested by any of its constituent disciplines, e.g., laptop science and statistics?” is a vital litmus take a look at for whether or not information science must be thought-about a science. Some questions rising from information science might really feel novel (Wing, 2020); nevertheless, even these typically cut back to functions of present disciplines (statistics, laptop science, optimization concept) relatively than point out a essentially new science.
Contributions from completely different disciplines could make information science richer. But, there’s mounting proof (Wilkerson, 2025) it is usually inflicting confusion for college kids, educators, and employers. There may be proof of necessary variations throughout undergraduate information science schooling, between information science schooling efforts for majors versus nonmajors, and between Ok–12 information science initiatives rising from completely different teams and disciplines.
Contributions from a number of disciplines don’t simply flow into within the absence of a centralized neighborhood (Dogucu et al., 2025) resulting in fragmentation. The interdisciplinary nature of knowledge science is turning into multidisciplinary. Quite a few skilled societies now have express information science, or intently associated, subgroups and focus areas. Area particular information science journals — Environmental Information Science and the Annual Evaluation of Biomedical Information Science to call a couple of — are wonderful shops for analysis; but, we could also be dropping the interactive and holistic facet of an interdisciplinary subject. Navigating your entire information science panorama is a problem. This additional manifests itself within the many distinct roles that seem throughout “Information Scientist” job ads (Saltz and Grady, 2017) and culminates within the “unicorn drawback” the place employers have the unrealistic expectation that one individual can grasp all the talents of what’s thought-about information science (Saltz and Grady, 2017).
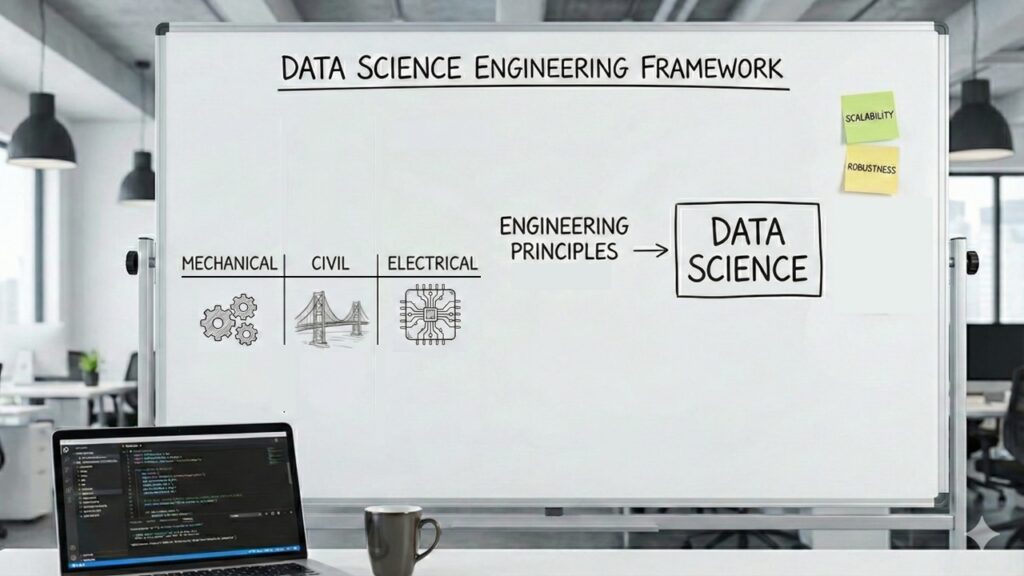
An Engineering Perspective
Wing’s questions (2020) reveal that information science has a essentially completely different relationship with area context than arithmetic, statistics, or laptop science. This completely different relationship — the place area is integral relatively than inspirational — is exactly what distinguishes engineering from science.
Domains encourage questions within the sciences, however the domains aren’t basic. Arithmetic research summary constructions, and we will do group concept with none utility in thoughts. Statistics research inference from information typically and we will develop a statistical concept with out a particular area. Laptop Science research computation abstractly and we will develop algorithms, complexity concept, and coding languages with out functions in thoughts. These fields are impressed by domains however exist independently of these domains.
Engineering, alternatively, can not exist with out utility context. Civil engineering actually can’t be studied with out contemplating what you’re constructing (bridges, dams, buildings). The area isn’t simply inspirational — it’s constitutive. We are able to’t train mechanical engineering as pure abstraction after which “add” functions later. Commerce-offs (e.g. algorithmic, effectivity, price) solely make sense throughout the engineer’s area constraints. Information science matches this mannequin.
A knowledge scientist’s job is extra analogous to a civil engineer designing a bridge than a physicist learning basic forces. The bridge must work given the supplies obtainable, the funds, the terrain, and security necessities — even when which means utilizing approximations relatively than excellent options. But, engineering disciplines may also generate foundational insights as byproducts with out that being their goal. Thermodynamics emerged partly from engineers attempting to construct higher steam engines∂. Info concept got here from engineers engaged on telecommunications. However the subject’s telos is constructing programs that work, not advancing foundational concept. A knowledge scientist who develops a mannequin that improves buyer retention by 5% has succeeded, even when they used off-the-shelf strategies and generated zero novel insights.
Information science is essentially about constructing issues that work in messy, real-world contexts. Like different engineering disciplines, it includes:
- Making pragmatic trade-offs (accuracy vs. interpretability vs. computational price)
- Working inside constraints (restricted information, computational sources, enterprise necessities)
- Integrating a number of strategies to resolve sensible issues
- Specializing in deployment, upkeep, and iteration
Maybe information science is greatest understood — and taught — utilizing an engineering framework. Maybe information science wants specializations analogous to mechanical, civil, and electrical engineers. This engineering framing is about epistemology and apply, not essentially organizational construction. Engineering is essentially about the way you method issues — constructing programs that work below constraints — not about departmental affiliation. Biomedical engineering is engineering whether or not it’s housed with mechanical engineering or in a medical college. What issues is that information science packages undertake engineering rules: rigorous foundations, specialised tracks, give attention to constructing relatively than pure discovery, {and professional} requirements. This could occur in statistics departments, laptop science departments, engineering colleges, or standalone information science departments. The bottom line is the academic philosophy and requirements, not the title of the division.
Current Engineering Foundations
We aren’t the primary to view information science as engineering. Stueur’s essay (2020) expertly famous that whereas information science was turning into the engineering of the twenty-first century, it was being taught in two very distinct approaches. The primary is the inferential framework in statistics, the place the aim is to make dependable statements about that world. That is in distinction with the computational studying concept, the place information is seen as examples, and the aim is to be taught a common idea. Stueur notes (2020) there isn’t a frequent epistemological basis by which all information scientists are educated. We’re increasing upon these preliminary requires frequent foundations and current ideas on what this might appear like for information science as an instructional self-discipline and a occupation.
Hoerl and Snee (2015) have argued for a brand new self-discipline, known as statistical engineering, for coping with massive, unstructured, complicated issues, combining a number of statistical instruments, plus different disciplines. Statistical engineering is the applying of statistical pondering to massive, unstructured, real-world issues. This name for a brand new self-discipline has led to the formation of the Worldwide Statistical Engineering Affiliation (ISEA). It could seem that ISEA views statistical engineering because the science of integrating and making use of strategies rigorously with information science being the apply of utilizing these strategies.
Pan and colleagues (2021) have urged engineering fields introduce information science ideas resembling machine studying and a give attention to statistics. They word that you will need to refine the college curriculum and practice engineers to make use of information science and be information literate from the outset (Pan et al., 2021). We imagine information science ought to undertake the reciprocal philosophy. Gerald Friedland has taken this to coronary heart by introducing a novel textbook (Friedland, 2023) presenting machine studying from an engineering perspective. It’s value noting that engineering views are showing in associated domains as effectively. Rebecca Willet (2019), for instance, has known as for an engineering method to synthetic intelligence.
Though the information science as engineering thought will not be new, there are nonetheless plenty of open questions. How ought to curricula change if we settle for that information science is engineering? What competencies ought to we emphasize? How can we train failure — not simply accuracy? Ought to information scientists have codes of apply like engineers do? Our aim is to proceed the dialogue of knowledge science as engineering whereas suggesting pedagogical, skilled, and moral views on these questions.
Implications for Schooling
Conventional engineering disciplines require deep foundational data exactly as a result of engineers want to acknowledge once they’re on the boundaries of established concept. A civil engineer wants to know supplies science and structural mechanics effectively sufficient to know when a design drawback requires new analysis versus when it’s a simple utility of recognized rules.
Equally, an information scientist engaged on, say, a brand new structure for time sequence prediction ought to ideally acknowledge: “This convergence conduct is bizarre — this is likely to be referring to one thing basic about optimization landscapes” versus “That is only a hyperparameter tuning subject.”
We need to keep away from schooling that generates practitioners who can use instruments however not acknowledge once they’re observing one thing that violates theoretical expectations — which is strictly when foundational insights emerge. A scarcity of specialization creates each a sign drawback (how do you assess practitioners?) and a coaching drawback (one curriculum can’t serve all wants).
Listed below are a couple of recommendations to help the continuing discussions on the information science curriculum.
- Core sequence in linear algebra and likelihood concept.
- Physics for perception — some publicity to statistical mechanics and data concept, framed round their connections to studying programs could be extraordinarily invaluable.
- “Foundations for practitioners” programs — Programs explicitly designed to offer practitioners sufficient theoretical grounding to acknowledge anomalies and foundational questions. Not a course in instrument X; relatively, “Right here’s what ought to occur based on concept, right here’s what it appears like whenever you’re outdoors the speculation.”
- Educate reliability, testing, and explainability as first-class ideas.
- Case research of foundational discoveries — Instructing by examples like “how dropout was found” or “why the Adam optimizer converges in a different way than concept predicted” to coach the ability of recognizing foundational questions.
- Introduce capstone “design labs” modeled after engineering senior design.
- A give attention to information ethics and equity.
What modifications within the classroom is a shift from a scientific framing — match a mannequin to foretell home costs — to an engineering framing — design a pricing mannequin that’s correct, explainable to regulators, and mechanically retrains when market situations shift. Now college students should contemplate pipelines, versioning, monitoring, and ethics — not simply imply absolute error. Engineering college students be taught that programs fail, and that design is iterative. Information science college students ought to too.
Ethics could be taught as a design constraint. Quite than tacking on ethics as a dialogue subject, it’s handled as a design parameter. If our programs should not produce disparate outcomes by gender or race then ethics turns into a technical design requirement, not an ethical afterthought.
In an engineering-style information science, instruments usually are not elective extras. Selecting the proper instruments for reproducibility, monitoring and deployment, automation, and documentation change into the equal of security codes and requirements in conventional engineering.
Our evaluation of scholars additionally shifts. As an alternative of grading solely accuracy or mathematical derivations, we consider robustness, readability of design, interpretability, and equity metrics. College students must be rewarded for constructing programs that final.
The shifts in pedagogy would give practitioners the power to:
- Learn theoretical papers and perceive what they’re claiming
- Acknowledge when empirical outcomes contradict theoretical expectations
- Have theoretical and bodily intuitions about algorithms
- Know when to seek the advice of deeper concept
- Talk with researchers in adjoining fields
- Study from system failure
To be clear, we’re not saying “reorganize all faculties and universities.” Quite, “acknowledge information science as an engineering apply and construction schooling accordingly”. Engineering is a mode of apply, not simply an organizational class. The engineering framing is about skilled id and academic requirements, not departmental location.
Proposed Specializations and Modifications to Skilled Societies
If information science is engineering, we should shift from the scientific mannequin (targeted on analysis dissemination and educational credentialing) to the engineering mannequin (targeted on skilled requirements, public accountability, and apply competence). This consists of specializations, enforceable ethics codes, technical requirements with regulatory implications, and academic accreditation. What may information science specializations appear like? Right here’s one doable breakdown to maneuver the dialog ahead.
Statistical/Experimental Information Scientist
- Instructional necessities: causal inference, experimental design, survey methodology
- Purposes: A/B testing, coverage analysis, scientific trials
- Math core: Actual evaluation, likelihood, statistics
- Restricted publicity to: Distributed programs, deep studying
AI/Machine Studying Information Scientist
- Instructional necessities: algorithms, distributed programs, optimization
- Purposes: Suggestion programs, search, large-scale prediction
- Math core: Linear algebra, optimization, some statistical mechanics
- Heavy publicity to: Software program engineering, MLOps, scalability
Scientific/Analysis Information Scientist
- Instructional necessities: area science + statistics
- Purposes: Genomics, local weather, physics, social science
- Math/Science core: physics, statistics, linear algebra, scientific computing
- Give attention to: Interpretability, uncertainty quantification, causal fashions
Enterprise Intelligence Information Scientist
- Instructional necessities: enterprise/economics, some statistics and Calculus
- Heavy on: SQL, visualization, communication, area data
- Purposes: Dashboards, reviews, exploratory evaluation
Information science packages {and professional} societies with an engineering focus would have information requirements analogous to engineering constructing codes. Not for the regulatory perform of constructing codes. Quite, the certification of instruments and approaches for business. This may consist of knowledge documentation requirements (what constitutes sufficient documentation), mannequin validation protocols (when is a mannequin prepared for deployment?), reproducibility requirements (minimal necessities for computational reproducibility), equity and bias testing protocols, and safety and privateness requirements for information dealing with. These shouldn’t be educational papers — they need to be dwelling requirements co-developed and adopted by business.
Membership and focus would additionally shift inside information science skilled societies. There could be equal house for practitioners, not simply educational analysis. Engineers be taught from failures (e.g. bridge collapses). Information science wants failure case research as effectively. Ethics, centered on penalties, would dominate educating and publication. Public welfare (when ought to an information scientist refuse to construct one thing?), downstream harms (accountability for a way fashions are deployed), and enforceable requirements (not simply aspirational) would take heart stage. Engineering ethics asks: “What might go improper and who might be harmed?” Information science ethics ought to do the identical.
Instructing information science as engineering redefines success from “mannequin accuracy” to “system reliability and accountability”. As our information programs form the world, we should practice information scientists not simply as analysts of knowledge however as engineers of knowledge system penalties.
Avoiding a False Dichotomy
The “science discovers, engineering applies” narrative is overly simplistic. Actuality is far richer. Historical past exhibits engineering and science intertwine with many foundational scientific insights emerged from engineering apply. The boundary is permeable and productive. Information science will generate new scientific insights and information scientists who make scientific discoveries are doing distinctive engineering, not abandoning engineering for science. On this regard, the title is basically of secondary concern as a result of an engineering framing values each forms of contributions. Whereas its pedagogy and professionalism acknowledge that almost all work is synthesis and utility, we must always nonetheless create house for discovery. It is a a lot more healthy mannequin than pretending all information scientists are doing basic science, or that those that construct programs are by some means lesser. Viewing information science as…
The engineering self-discipline that applies statistical, computational, and area data to design data-driven programs that function successfully and ethically in apply
…clarifies why information scientists worth pipelines and scalability, why reproducibility and maintainability matter, and why information science doesn’t must invent new math to be an actual subject. Once we see information science as engineering, we cease asking “Which mannequin is greatest?” and begin asking “Which system design solves this drawback responsibly and sustainably?” That shift produces practitioners who can suppose end-to-end, balancing concept, computation, and ethics — very like civil engineers stability physics, supplies, and security.
Acknowledgements
The writer wish to thank Dr. Invoice More durable (Director of College Growth and Instructing Excellence) and Dr. Rodney Yoder (Affiliate Professor of Physics and Engineering Science) for useful discussions and suggestions on this text.
References
Blei, D. M. and Smyth, P. (2017). Science and information science. Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, 114(33), 8689–8692.
Cleveland, W. S., (2001). Information Science: an motion plan for increasing the technical areas of the sector of statistics. Worldwide statistical evaluate, 69(1):21–26
Dogucu, M., Demirci, S., Bendekgey, H., Ricci, F. Z., and Medina, C. M. (2025). A Systematic Literature Evaluation of Undergraduate Information Science Schooling Analysis. Journal of Statistics and Information Science Schooling, 33(4), 459-471.
Donoho, D. (2017). 50 Years of Information Science. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 26(4), 745-766.
Friedland, G. (2024), Info-Pushed Machine Studying, Springer Cham, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-39477-5
Hoerl, R. W. and Snee, R. D. (2015), Statistical Engineering: An Thought Whose Time Has Come?, arXiv preprint, https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06013
Meng, X.-L. (2019). Information Science: An Synthetic Ecosystem. Harvard Information Science Evaluation, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.ba20f892
Pan, I., Mason, L., and Matar, M. (2021), Information-Centric Engineering: integrating simulation, machine studying and statistics. Challenges and Alternatives, arXiv preprint, https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06223
Saltz, J. S. and Grady, N. W. (2017). The paradox of knowledge science workforce roles and the necessity for an information science workforce framework. 2017 IEEE Worldwide Convention on Massive Information (Massive Information), Boston, MA, USA, 2017, pp. 2355-2361, doi: 10.1109/BigData.2017.8258190.
Steuer, D. (2020), Time for Information Science to Professionalise, Significance, Quantity 17, Situation 4, August 2020, Pages 44–45, https://doi.org/10.1111/1740-9713.01430
Wilkerson, M. H. (2025). Mapping the Conceptual Basis(s) of ‘Information Science Schooling.’ Harvard Information Science Evaluation, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.9ac68105
Willett, R. (2019). Engineering Views on AI. Harvard Information Science Evaluation, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.98280d4a
Wing, J.M., Janeia, V.P., Kloefkorn, T., & Erickson, L.C. (2018). Information Science Management Summit, Workshop Report, Nationwide Science Basis. Retrieved from https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3293458
Wing, J. M. (2020). Ten Analysis Problem Areas in Information Science. Harvard Information Science Evaluation, 2(3). https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.c6577b1f