The alerts that drive most of the mind and physique’s most important capabilities — consciousness, sleep, respiration, coronary heart price, and movement — course by bundles of “white matter” fibers within the brainstem, however imaging methods to this point have been unable to finely resolve these essential neural cables. That has left researchers and docs with little functionality to evaluate how they’re affected by trauma or neurodegeneration.
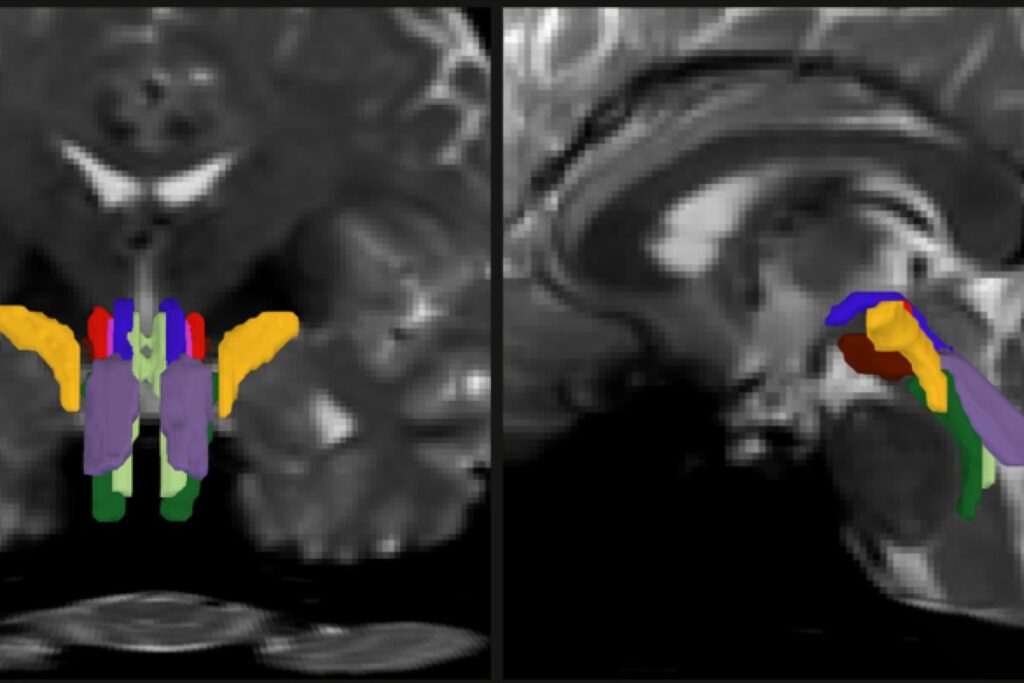
In a brand new research, a workforce of MIT, Harvard College, and Massachusetts Basic Hospital researchers unveil AI-powered software program able to mechanically segmenting eight distinct bundles in any diffusion MRI sequence.
Within the open-access research, published Feb. 6 in the Proceedings of the National Academy Sciences, the analysis workforce led by MIT graduate scholar Mark Olchanyi experiences that their BrainStem Bundle Device (BSBT), which they’ve made publicly available, revealed distinct patterns of structural modifications in sufferers with Parkinson’s illness, a number of sclerosis, and traumatic mind harm, and make clear Alzheimer’s illness as nicely. Furthermore, the research exhibits, BSBT retrospectively enabled monitoring of bundle therapeutic in a coma affected person that mirrored the affected person’s seven-month highway to restoration.
“The brainstem is a area of the mind that’s primarily not explored as a result of it’s powerful to picture,” says Olchanyi, a doctoral candidate in MIT’s Medical Engineering and Medical Physics Program. “Folks do not actually perceive its make-up from an imaging perspective. We have to perceive what the group of the white matter is in people and the way this group breaks down in sure issues.”
Provides Professor Emery N. Brown, Olchanyi’s thesis supervisor and co-senior writer of the research, “the brainstem is likely one of the physique’s most essential management facilities. Mark’s algorithms are a major contribution to imaging analysis and to our skill to the perceive regulation of basic physiology. By enhancing our capability to picture the brainstem, he presents us new entry to important physiological capabilities comparable to management of the respiratory and cardiovascular methods, temperature regulation, how we keep awake in the course of the day and the way sleep at night time.”
Brown is the Edward Hood Taplin Professor of Computational Neuroscience and Medical Engineering in The Picower Institute for Studying and Reminiscence, the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science, and the Division of Mind and Cognitive Sciences at MIT. He’s additionally an anesthesiologist at MGH and a professor at Harvard Medical Faculty.
Constructing the algorithm
Diffusion MRI helps hint the lengthy branches, or “axons,” that neurons lengthen to speak with one another. Axons are usually clad in a sheath of fats referred to as myelin, and water diffuses alongside the axons throughout the myelin, which can also be referred to as the mind’s “white matter.” Diffusion MRI can spotlight this very directed displacement of water. However segmenting the distinct bundles of axons within the brainstem has proved difficult, as a result of they’re small and masked by flows of mind fluids and the motions produced by respiration and coronary heart beats.
As a part of his thesis work to raised perceive the neural mechanisms that underpin consciousness, Olchanyi wished to develop an AI algorithm to beat these obstacles. BSBT works by tracing fiber bundles that plunge into the brainstem from neighboring areas increased within the mind, such because the thalamus and the cerebellum, to supply a “probabilistic fiber map.” A man-made intelligence module referred to as a “convolutional neural community” then combines the map with a number of channels of imaging data from throughout the brainstem to tell apart eight particular person bundles.
To coach the neural community to section the bundles, Olchanyi “confirmed” it 30 dwell diffusion MRI scans from volunteers within the Human Connectome Mission (HCP). The scans had been manually annotated to show the neural community find out how to determine the bundles. Then he validated BSBT by testing its output towards “floor reality” dissections of autopsy human brains the place the bundles had been nicely delineated by way of microscopic inspection or very gradual however ultra-high-resolution imaging. After coaching, BSBT grew to become proficient in mechanically figuring out the eight distinct fiber bundles in new scans.
In an experiment to check its consistency and reliability, Olchanyi tasked BSBT with discovering the bundles in 40 volunteers who underwent separate scans two months aside. In every case, the device was capable of finding the identical bundles in the identical sufferers in every of their two scans. Olchanyi additionally examined BSBT with a number of datasets (not simply the HCP), and even inspected how every element of the neural community contributed to BSBT’s evaluation by hobbling them one after the other.
“We put the neural community by the wringer,” Olchanyi says. “We wished to be sure that it’s truly doing these believable segmentations and it’s leveraging every of its particular person parts in a approach that improves the accuracy.”
Potential novel biomarkers
As soon as the algorithm was correctly skilled and validated, the analysis workforce moved on to testing whether or not the power to section distinct fiber bundles in diffusion MRI scans might allow monitoring of how every bundle’s quantity and construction different with illness or harm, making a novel form of biomarker. Though the brainstem has been troublesome to look at intimately, many research present that neurodegenerative ailments have an effect on the brainstem, usually early on of their development.
Olchanyi, Brown and their co-authors utilized BSBT to scores of datasets of diffusion MRI scans from sufferers with Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, MS, and traumatic mind harm (TBI). Sufferers had been in comparison with controls and generally to themselves over time. Within the scans, the device measured bundle quantity and “fractional anisotropy,” (FA) which tracks how a lot water is flowing alongside the myelinated axons versus how a lot is diffusing in different instructions, a proxy for white matter structural integrity.
In every situation, the device discovered constant patterns of modifications within the bundles. Whereas just one bundle confirmed vital decline in Alzheimer’s, in Parkinson’s the device revealed a discount in FA in three of the eight bundles. It additionally revealed quantity loss in one other bundle in sufferers between a baseline scan and a two-year follow-up. Sufferers with MS confirmed their best FA reductions in 4 bundles and quantity loss in three. In the meantime, TBI sufferers didn’t present vital quantity loss in any bundles, however FA reductions had been obvious within the majority of bundles.
Testing within the research confirmed that BSBT proved extra correct than different classifier strategies in discriminating between sufferers with well being circumstances versus controls.
BSBT, due to this fact, may be “a key adjunct that aids present diagnostic imaging strategies by offering a fine-grained evaluation of brainstem white matter construction and, in some instances, longitudinal data,” the authors wrote.
Lastly, within the case of a 29-year-old man who suffered a extreme TBI, Olchanyi utilized BSBT to a scans taken in the course of the man’s seven-month coma. The device confirmed that the person’s brainstem bundles had been displaced, however not reduce, and confirmed that over his coma, the lesions on the nerve bundles decreased by an element of three in quantity. As they healed, the bundles moved again into place as nicely.
The authors wrote that BSBT “has substantial prognostic potential by figuring out preserved brainstem bundles that may facilitate coma restoration.”
The research’s different senior authors are Juan Eugenio Iglesias and Brian Edlow. Different co-authors are David Schreier, Jian Li, Chiara Maffei, Annabel Sorby-Adams, Hannah Kinney, Brian Healy, Holly Freeman, Jared Shless, Christophe Destrieux, and Hendry Tregidgo.
Funding for the research got here from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, U.S. Division of Protection, James S. McDonnell Basis, Rappaport Basis, American SidS Institute, American Mind Basis, American Academy of Neurology, Heart for Integration of Drugs and Progressive Know-how, Blueprint for Neuroscience Analysis, and Massachusetts Life Sciences Heart.