In Part 1 of this sequence, how Azure and AWS take essentially totally different approaches to machine studying challenge administration and knowledge storage.
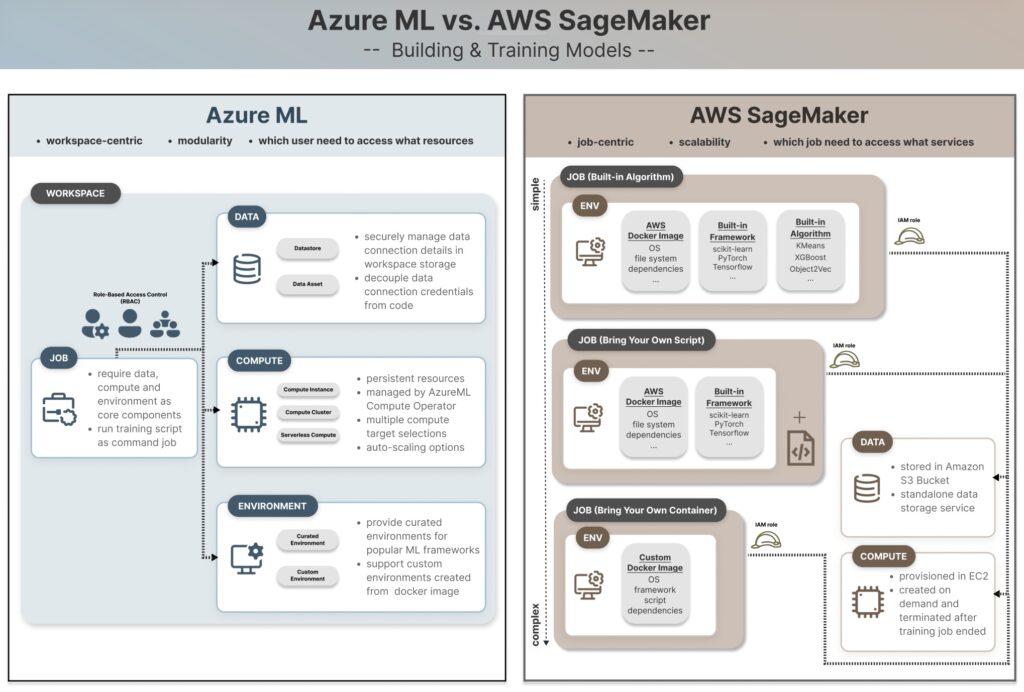
Azure ML makes use of a workspace-centric construction with user-level role-based entry management (RBAC), the place permissions are granted to people based mostly on their duties. In distinction, AWS SageMaker adopts a job-centric structure that decouples person permissions from job execution, granting entry on the job degree by IAM roles. For knowledge storage, Azure ML depends on datastores and knowledge belongings inside workspaces to handle connections and credentials behind the scenes, whereas AWS SageMaker integrates immediately with S3 buckets, requiring express permission grants for SageMaker execution roles to entry knowledge.
Discover out extra on this article:
Having established how these platforms deal with challenge setup and knowledge entry, in Half 2, we’ll study the compute assets and runtime environments that energy the mannequin coaching jobs.
Compute
Compute is the digital machine the place your mannequin and code run. Together with community and storage, it is likely one of the basic constructing blocks of cloud computing. Compute assets usually symbolize the most important price part of an ML challenge, as coaching fashions—particularly massive AI fashions—requires lengthy coaching instances and infrequently specialised compute situations (e.g., GPU situations) with increased prices. Subsequently, Azure ML designs a devoted AzureML Compute Operator function (see particulars in Part 1) for managing compute assets.
Azure and AWS supply numerous occasion varieties that differ within the variety of CPUs/GPUs, reminiscence, disk house and kind, every designed for particular functions. Each platforms use a pay-as-you-go pricing mannequin, charging just for energetic compute time.
Azure virtual machine series are named in alphabetic order; as an example, D household VMs are designed for general-purpose workloads and meet the necessities for many growth and manufacturing environments. AWS compute instances are additionally grouped into households based mostly on their objective; as an example, the m5 household comprises general-purpose situations for SageMaker ML growth. The desk beneath compares compute situations supplied by Azure and AWS based mostly on their objective, hourly pricing and typical use circumstances. (Please word that the pricing construction varies by area and plan, so I like to recommend trying out their official web sites.)
Now that we’ve in contrast compute pricing in AWS and Azure, let’s discover how the 2 platforms differ in integrating compute assets into ML methods.
Azure ML

Computes are persistent assets within the Azure ML Workspace, usually created as soon as by the AzureML Compute Operator and reused by the info science crew. Since compute assets are cost-intensive, this construction permits them to be centrally managed by a task with cloud infrastructure experience, whereas knowledge scientists and engineers can deal with growth work.
Azure provides a spectrum of compute goal choices designated for ML growth and deployment, relying on the dimensions of the workload. A compute occasion is a single-node machine appropriate for interactive growth and testing within the Jupyter pocket book surroundings. A compute cluster is one other sort of compute goal that spins up multi-node cluster machines. It may be scaled for parallel processing based mostly on workload demand and helps auto-scaling by configuring the parameter min_instances and max_instances. Moreover, there are severless compute, Kubernetes clusters, and containers which might be match for various functions. Here’s a helpful visible abstract that helps you make the choice based mostly in your use case.
” image from “[Explore and configure the Azure Machine Learning workspace DP-100](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_f5dlIvI5LQ)”](https://contributor.insightmediagroup.io/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/image-2-1024x477.png)
To create an Azure ML managed compute goal we create an AmlCompute object utilizing the code beneath:
sort: use"amlcompute"for compute cluster. Alternatively, use"computeinstance"for single-node interactive growth and“kubernetes"for AKS clusters.identify: specify the compute goal identify.dimension: specify the occasion dimension.min_instancesandmax_instances(elective): set the vary of situations allowed to run concurrently.idle_time_before_scale_down(elective): routinely shut down the compute cluster when idle to keep away from incurring pointless prices.
# Create a compute cluster
cpu_cluster = AmlCompute(
identify="cpu-cluster",
sort="amlcompute",
dimension="Standard_DS3_v2",
min_instances=0,
max_instances=4,
idle_time_before_scale_down=120
)
# Create or replace the compute
ml_client.compute.begin_create_or_update(cpu_cluster)As soon as the compute useful resource is created, anybody within the shared Workspace can use it by merely referencing its identify in an ML job, making it simply accessible for crew collaboration.
# Use the endured compute "cpu-cluster" within the job
job = command(
code='./src',
command='python code.py',
compute='cpu-cluster',
display_name='train-custom-env',
experiment_name='coaching'
)AWS SageMaker AI

Compute assets are managed by a standalone AWS service – EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud). When utilizing these compute assets in SageMaker, it require builders to explicitly configure the occasion sort for every job, then compute situations are created on-demand and terminated when the job finishes. This strategy offers builders extra flexibility over compute choice based mostly on activity, however requires extra infrastructure information to pick and handle the suitable compute useful resource. For instance, obtainable occasion varieties differ by job sort. ml.t3.medium and ml.t3.massive are generally used for powering SageMaker notebooks in interactive growth environments, however they aren’t obtainable for coaching jobs, which require extra highly effective occasion varieties from the m5, c5, p3, or g4dn households.
As proven within the code snippet beneath, AWS SageMaker specifies the compute occasion and the variety of situations working concurrently as job parameters. A compute occasion with the ml.m5.xlarge sort is created throughout job execution and charged based mostly on the job runtime.
estimator = Estimator(
image_uri=image_uri,
function=function,
instance_type="ml.m5.xlarge",
instance_count=1
)SageMaker jobs spin up on-demand situations by default. They’re charged by seconds and gives assured capability for working time-sensitive jobs. For jobs that may tolerate interruptions and better latency, spot occasion is a extra cost-saving choice that makes use of unused compute situations. The draw back is the extra ready interval when there aren’t any obtainable spot situations. We use the code snippet beneath to implement a spot occasion choice for a coaching job.
use_spot_instances: set asTrueto make use of spot situations, in any other case default to on-demandmax_wait: the utmost period of time you’re prepared to attend for obtainable spot situations (ready time isn’t charged)max_run: the utmost quantity of coaching time allowed for the jobcheckpoint_s3_uri: the S3 bucket URI path to save lots of mannequin checkpoints, in order that coaching can safely restart after ready
estimator = Estimator(
image_uri=image_uri,
function=function,
instance_type="ml.m5.xlarge",
instance_count=1,
use_spot_instances=True,
max_run=3600,
max_wait=7200,
checkpoint_s3_uri="<s3://demo-bucket/mannequin/checkpoints>"
)What does this imply in apply?
- Azure ML: Azure’s persistent compute strategy permits centralized administration and sharing throughout a number of builders, permitting knowledge scientists to deal with mannequin growth quite than infrastructure administration.
- AWS SageMaker AI: SageMaker requires builders to explicitly outline compute occasion sort for every job, offering extra flexibility but additionally demanding deeper infrastructure information of occasion varieties, prices and availability constraints.
Reference
Atmosphere
Atmosphere defines the place the code or job is run, together with software program, working system, program packages, docker picture and surroundings variables. Whereas compute is accountable for the underlying infrastructure and {hardware} choices, surroundings setup is essential in guaranteeing constant and reproducible behaviors throughout growth and manufacturing surroundings, mitigating package deal conflicts and dependency points when executing the identical code in several runtime setup by totally different builders. Azure ML and SageMaker each assist utilizing their curated environments and organising {custom} environments.
Azure ML
Just like Knowledge and Compute, Atmosphere is taken into account a sort of useful resource and asset within the Azure ML Workspace. Azure ML provides a complete checklist of curated environments for widespread python frameworks (e.g. PyTorch, Tensorflow, scikit-learn) designed for CPU or GPU/CUDA goal.
The code snippet beneath helps to retrieve the checklist of all curated environments in Azure ML. They often comply with a naming conference that features the framework identify, model, working system, Python model, and compute goal (CPU/GPU), e.g.AzureML-sklearn-1.0-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu signifies scikit-learn model 1.0, working on Ubuntu 20.04 with Python 3.8 for CPU compute.
envs = ml_client.environments.checklist()
for env in envs:
print(env.identify)
# >>> Auzre ML Curated Environments
"""
AzureML-AI-Studio-Growth
AzureML-ACPT-pytorch-1.13-py38-cuda11.7-gpu
AzureML-ACPT-pytorch-1.12-py38-cuda11.6-gpu
AzureML-ACPT-pytorch-1.12-py39-cuda11.6-gpu
AzureML-ACPT-pytorch-1.11-py38-cuda11.5-gpu
AzureML-ACPT-pytorch-1.11-py38-cuda11.3-gpu
AzureML-responsibleai-0.21-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu
AzureML-responsibleai-0.20-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu
AzureML-tensorflow-2.5-ubuntu20.04-py38-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-tensorflow-2.6-ubuntu20.04-py38-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-tensorflow-2.7-ubuntu20.04-py38-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-sklearn-1.0-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu
AzureML-pytorch-1.10-ubuntu18.04-py38-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-pytorch-1.9-ubuntu18.04-py37-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-pytorch-1.8-ubuntu18.04-py37-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-sklearn-0.24-ubuntu18.04-py37-cpu
AzureML-lightgbm-3.2-ubuntu18.04-py37-cpu
AzureML-pytorch-1.7-ubuntu18.04-py37-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-tensorflow-2.4-ubuntu18.04-py37-cuda11-gpu
AzureML-Triton
AzureML-Designer-Rating
AzureML-VowpalWabbit-8.8.0
AzureML-PyTorch-1.3-CPU
"""
To run the coaching job in a curated surroundings, we create an surroundings object by referencing its identify and model, then passing it as a job parameter.
# Get an curated Atmosphere
surroundings = ml_client.environments.get("AzureML-sklearn-1.0-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu", model=44)
# Use the curated surroundings in Job
job = command(
code=".",
command="python practice.py",
surroundings=surroundings,
compute="cpu-cluster"
)
ml_client.jobs.create_or_update(job)Alternatively, create a {custom} surroundings from a Docker picture registered in Docker Hob utilizing the code snippet beneath.
# Get an curated Atmosphere
surroundings = ml_client.environments.get("AzureML-sklearn-1.0-ubuntu20.04-py38-cpu", model=44)
# Use the curated surroundings in Job
job = command(
code=".",
command="python practice.py",
surroundings=surroundings,
compute="cpu-cluster"
)
ml_client.jobs.create_or_update(job)AWS SageMaker AI
SageMaker’s surroundings configuration is tightly coupled with job definitions, providing three ranges of customization to determine the OS, frameworks and packages required for job execution. These are Constructed-in Algorithm, Deliver Your Personal Script (Script mode) and Deliver Your Personal Container (BYOC), starting from the simplest but inflexible choice to essentially the most complicated but customizable choice.
Constructed-in Algorithms

That is the choice with the least quantity of effort for builders to coach and deploy machine studying fashions at scale in AWS SageMaker and Azure at the moment doesn’t supply an equal built-in algorithm strategy utilizing Python SDK as of February 2026.
SageMaker encapsulates the machine studying algorithm, in addition to its python library and framework dependencies inside an estimator object. For instance, right here we instantiate a KMeans estimator by specifying the algorithm-specific hyperparameter okay and passing the coaching knowledge to suit the mannequin. Then the coaching job will spin up a ml.m5.massive compute occasion and the educated mannequin might be saved within the output location.
Deliver Your Personal Script

The convey your individual script strategy (also called script mode or convey your individual mannequin) permits builders to leverage SageMaker’s prebuilt containers for widespread python frameworks for machine studying like scikit-learn, PyTorch and Tensorflow. It gives the flexibleness of customizing the coaching job by your individual script with out the necessity of managing the job execution surroundings, making it the preferred selection when utilizing specialised algorithms not included in SageMaker’s built-in choices.
Within the instance beneath, we instantiate an estimator utilizing the scikit-learn framework by offering a {custom} coaching script train.py, the mannequin’s hyperparameters, together with the framework model and python model.
from sagemaker.sklearn import SKLearn
sk_estimator = SKLearn(
entry_point="practice.py",
function=function,
instance_count=1,
instance_type="ml.m5.massive",
py_version="py3",
framework_version="1.2-1",
script_mode=True,
hyperparameters={"estimators": 20},
)
# Prepare the estimator
sk_estimator.match({"practice": training_data})Deliver Your Personal Container
That is the strategy with the best degree of customization, which permits builders to convey a {custom} surroundings utilizing a Docker picture. It fits situations that depend on unsupported python frameworks, specialised packages, or different programming languages (e.g. R, Java and many others). The workflow entails constructing a Docker picture that comprises all required package deal dependencies and mannequin coaching scripts, then push it to Elastic Container Registry (ECR), which is AWS’s container registry service equal to Docker Hub.
Within the code beneath, we specify the {custom} docker picture URI as a parameter to create the estimator and match the estimator with coaching knowledge.
from sagemaker.estimator import Estimator
image_uri = "<your-dkr-ecr-image-uri>:<tag>"
byoc_estimator = Estimator(
image_uri=image_uri,
function=function,
instance_count=1,
instance_type="ml.m5.massive",
output_path="<s3://demo-bucket/mannequin/>",
sagemaker_session=sess,
)
byoc_estimator.match(training_data)What does it imply in apply?
- Azure ML: Gives assist for working coaching jobs utilizing its intensive assortment of curated environments that cowl widespread frameworks corresponding to PyTorch, TensorFlow, and scikit-learn, in addition to providing the aptitude to construct and configure {custom} environments from Docker photos for extra specialised use circumstances. Nonetheless, it is very important word that Azure ML doesn’t at the moment supply the built-in algorithm strategy that encapsulates and packages widespread machine studying algorithms immediately into the surroundings in the identical manner that SageMaker does.
- AWS SageMaker AI: SageMaker is understood for its three degree of customizations—Constructed-in Algorithm, Deliver Your Personal Script, Deliver Your Personal Container—which cowl a spectrum of builders necessities. Constructed-in Algorithm and Deliver Your Personal Script use AWS’s managed environments and combine tightly with ML algorithms or frameworks. They provide simplicity however are much less appropriate for extremely specialised mannequin coaching processes.
In Abstract
Based mostly on the comparisons of Compute and Atmosphere above together with what we mentioned in AWS vs. Azure: A Deep Dive into Model Training — Part 1 (Mission Setup and Knowledge Storage), we might have realized the 2 platforms undertake totally different design rules to construction their machine studying ecosystems.
Azure ML follows a extra modular structure the place Knowledge, Compute, and Atmosphere are handled as unbiased assets and belongings throughout the Azure ML Workspace. Since they are often configured and managed individually, this strategy is extra beginner-friendly, particularly for customers with out intensive cloud computing or permission administration information. For example, a knowledge scientist can create a coaching job by attaching an current compute within the Workspace while not having infrastructural experience to handle compute situations.
AWS SageMaker has a steeper studying curve, as a number of providers are tightly coupled and orchestrated collectively as a holistic system for ML job execution. Nonetheless, this job-centric strategy provides clear separation between mannequin coaching and mannequin deployment environments, in addition to the flexibility for distributed coaching at scale. By giving builders extra infrastructure management, SageMaker is effectively fitted to large-scale knowledge science and AI groups with excessive MLOps maturity and the necessity of CI/CD pipelines.
Take-House Message
On this sequence, we evaluate the 2 hottest cloud platforms Azure and AWS for scalable mannequin coaching, breaking down the comparability into the next dimensions:
- Mission and Permission Administration
- Knowledge storage
- Compute
- Atmosphere
In Part 1, we mentioned high-level challenge setup and permission administration, then talked about storing and accessing the info required for mannequin coaching.
In Half 2, we examined how Azure ML’s persistent, workspace-centric compute assets differ from AWS SageMaker’s on-demand, job-specific strategy. Moreover, we explored surroundings customization choices, from Azure’s curated environments and {custom} environments to SageMaker’s three degree of customizations—Constructed-in Algorithm, Deliver Your Personal Script, Deliver Your Personal Container. This comparability reveals Azure ML’s modular, beginner-friendly structure vs. SageMaker’s built-in, job-centric design that provides better scalability and infrastructure management for groups with MLOps necessities.