In the previous article, we explored distance-based clustering with Ok-Means.
additional: to enhance how the gap may be measured we add variance, to be able to get the Mahalanobis distance.
So, if k-Means is the unsupervised model of the Nearest Centroid classifier, then the pure query is:
What’s the unsupervised model of QDA?
Which means that like QDA, every cluster now needs to be described not solely by its imply, but in addition by its variance (and we even have so as to add covariance if the variety of options is greater than 2). However right here the whole lot is discovered with out labels.
So that you see the concept, proper?
And effectively, the title of this mannequin is the Gaussian Combination Mannequin (GMM)…
GMM and the names of those fashions…
As it’s typically the case, the names of the fashions come from historic causes. They don’t seem to be at all times designed to spotlight the connections between fashions, if they don’t seem to be discovered collectively.
Completely different researchers, totally different intervals, totally different use circumstances… and we find yourself with names that typically cover the true construction behind the concepts.
Right here, the title “Gaussian Combination Mannequin” merely signifies that the information is represented as a combination of a number of Gaussian distributions.
If we comply with the identical naming logic as k-Means, it will have been clearer to name it one thing like k-Gaussian Combination
As a result of, in apply, as an alternative of solely utilizing the means, we add the variance. And we may simply use the Mahalanobis distance, or one other weighted distance utilizing each means and variance. However Gaussian distribution offers us chances which might be simpler to interpret.
So we select a quantity okay of Gaussian parts.
And by the way in which, GMM isn’t the one one.
In reality, all the machine studying framework is definitely rather more current than lots of the fashions it comprises. Most of those methods have been initially developed in statistics, sign processing, econometrics, or sample recognition.
Then, a lot later, the sphere we now name “machine studying” emerged and regrouped all these fashions below one umbrella. However the names didn’t change.
So right this moment we use a mix of vocabularies coming from totally different eras, totally different communities, and totally different intentions.
Because of this the relationships between fashions should not at all times apparent if you look solely on the names.
If we needed to rename the whole lot with a contemporary, unified machine-learning type, the panorama would truly be a lot clearer:
- GMM would develop into k-Gaussian Clustering
- QDA would develop into Nearest Gaussian Classifier
- LDA, effectively, Nearest Gaussian Classifier with the identical variance throughout courses.
And abruptly, all of the hyperlinks seem:
- k-Means ↔ Nearest Centroid
- GMM ↔ Nearest Gaussian (QDA)
Because of this GMM is so pure after Ok-Means. If Ok-Means teams factors by their closest centroid, then GMM teams them by their closest Gaussian form.
Why this whole part to debate the names?
Effectively, the reality is that, since we already coated the k-means algorithm, and we already did the transition from Nearest Centroids Classifier to QDA, we already know all about this algorithm, and the coaching algorithm is not going to change…
And what’s the NAME of this coaching algorithm?
Oh, Lloyd’s algorithm.
Truly, earlier than k-means was known as so, it was merely often known as Lloyd’s algorithm, printed by Stuart Lloyd in 1957. Solely later, the machine studying neighborhood modified it to “k-means”.
And this algorithm manipulated solely the means, so we want one other title, proper?
You see the place that is going: the Expectation-Maximizing algorithm!
EM is just the overall type of Lloyd’s concept. Lloyd updates the means, EM updates the whole lot: means, variances, weights, and chances.
So, you already know the whole lot about GMM!
However since my article is known as “GMM in Excel”, I can’t finish my article right here…
GMM in 1 Dimension
Allow us to begin with this straightforward dataset, the identical we used for k-means: 1, 2, 3, 11, 12, 13
Hmm, the 2 Gaussians could have the identical variances. So take into consideration enjoying with different numbers in Excel!
And we naturally need 2 clusters.
Listed here are the totally different steps.
Initialization
We begin with guesses for means, variances, and weights.
Expectation step (E-step)
For every level, we compute how probably it’s to belong to every Gaussian.

Maximization step (M-step)
Utilizing these chances, we replace the means, variances, and weights.

Iteration
We repeat E-step and M-step till the parameters stabilise.

Every step is very simple as soon as the formulation are seen.
You will note that EM is nothing greater than updating averages, variances, and chances.
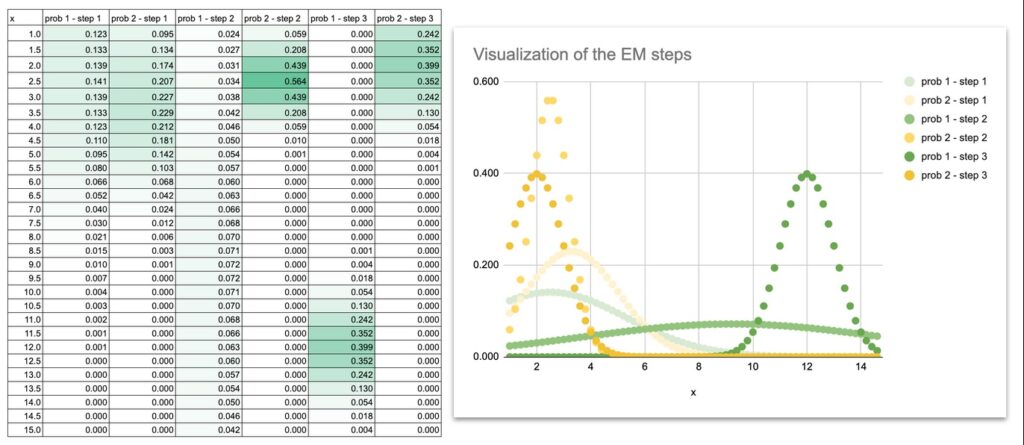
We are able to additionally do some visualization to see how the Gaussian curves transfer throughout the iterations.
At the start, the 2 Gaussian curves overlap closely as a result of the preliminary means and variances are simply guesses.
The curves slowly separate, modify their widths, and at last settle precisely on the 2 teams of factors.
By plotting the Gaussian curves at every iteration, you may actually watch the mannequin be taught:
- the means slide towards the facilities of the information
- the variances shrink to match the unfold of every group
- the overlap disappears
- the ultimate shapes match the construction of the dataset
This visible evolution is extraordinarily useful for instinct. When you see the curves transfer, EM is not an summary algorithm. It turns into a dynamic course of you may comply with step-by-step.

GMM in 2 Dimensions
The logic is precisely the identical as in 1D. Nothing new conceptually. We merely prolong the formulation…
As a substitute of getting one characteristic per level, we now have two.
Every Gaussian should now be taught:
- a imply for x1
- a imply for x2
- a variance for x1
- a variance for x2
- AND a covariance time period between the 2 options.
When you write the formulation in Excel, you will note that the method stays precisely the identical:
Effectively, the reality is that when you take a look at the screenshot, you may assume: “Wow, the system is so lengthy!” And this isn’t all of it.

However don’t be fooled. The system is lengthy solely as a result of we write out the 2-dimensional Gaussian density explicitly:
- one half for the gap in x1
- one half for the gap in x2
- the covariance time period
- the normalization fixed
Nothing extra.
It’s merely the density system expanded cell by cell.
Lengthy to sort, however completely comprehensible when you see the construction: a weighted distance, inside an exponential, divided by the determinant.
So sure, the system appears massive… however the concept behind this can be very easy.
Conclusion
Ok-Means offers laborious boundaries.
GMM offers chances.
As soon as the EM formulation are written in Excel, the mannequin turns into easy to comply with: the means transfer, the variances modify, and the Gaussians naturally settle across the information.
GMM is simply the following logical step after k-Means, providing a extra versatile strategy to symbolize clusters and their shapes.