or Claude to “search the online,” it isn’t simply answering from its coaching knowledge. It’s calling a separate search system.
Most individuals know that half.
What’s much less clear is how a lot conventional engines like google matter and the way a lot has been constructed on prime of them.
All of it isn’t totally public, so I’m performing some psychological deduction right here. However we are able to use totally different hints from taking a look at bigger techniques to construct a helpful psychological mannequin.
We’ll undergo question optimization, how engines like google are used for discovery, chunking content material, “on-the-fly” retrieval, and the way you may probably reverse-engineer a system like this to construct a “GEO [] scoring system.”
In case you’re accustomed to RAG, a few of this will likely be repetition, however it might probably nonetheless be helpful to see how bigger techniques cut up the pipeline right into a discovery part and a retrieval part.
In case you’re brief on time, you’ll be able to learn the TL;DR.
TL;DR
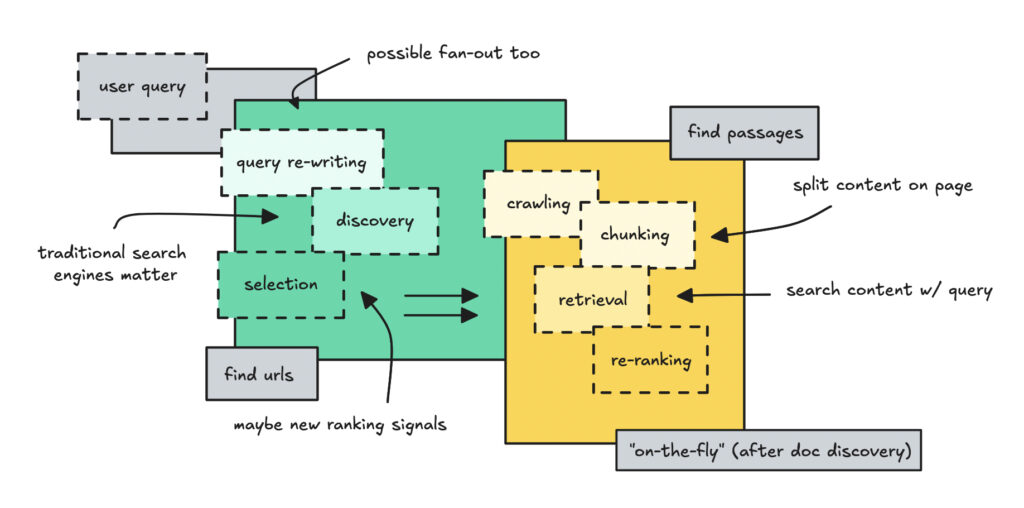
Internet search in these AI chatbots is probably going a two-part course of. The primary half leans on conventional engines like google to search out and rank candidate docs. Within the second half, they fetch the content material from these URLs and pull out essentially the most related passages utilizing passage-level retrieval.
The massive change (from conventional search engine optimization) is question rewriting and passage-level chunking, which let lower-ranked pages outrank increased ones if their particular paragraphs match the query higher.
The technical course of
The businesses behind Claude and ChatGPT aren’t totally clear about how their net search techniques work throughout the UI chat, however we are able to infer lots by piecing issues collectively.
We all know they lean on engines like google to search out candidates, at this scale, it will be absurd to not. We additionally know that what the LLM really sees are items of textual content (chunks or passages) when grounding their reply.
This strongly hints at some form of embedding-based retrieval over these chunks quite than over full pages.
This course of has a number of elements, so we’ll undergo it step-by-step.
Question re-writing & fan-out
First, we’ll take a look at how the system cleans up human queries and expands them. We’ll cowl the rewrite step, the fan-out step, and why this issues for each engineering and search engine optimization.
I believe this half may be essentially the most clear, and the one most individuals appear to agree on on-line.
The question optimization step is about taking a human question and turning it into one thing extra exact. For instance, “please seek for these purple footwear we talked about earlier” turns into “brown-red Nike sneakers.”
The fan-out step, then again, is about producing further rewrites. So if a person asks about climbing routes close to me, the system would possibly strive issues like “newbie hikes close to Stockholm,” “day hikes close to Stockholm public transport,” or “family-friendly trails close to Stockholm.”
That is totally different from simply utilizing synonyms, which conventional engines like google are already optimized for.
If that is the primary time you’re listening to about it and also you’re unconvinced, check out Google’s personal docs on AI query fan-out or do a little bit of digging round question rewriting.
To what extent this really works, we are able to’t know. They could not fan it out that a lot and simply work with a single question, then ship further ones down the pipeline if the outcomes are lackluster.
What we can say is that it’s most likely not a giant mannequin doing this half. In case you take a look at the analysis, Ye et al. explicitly use an LLM to generate sturdy rewrites, then distill that right into a smaller rewriter to keep away from latency and value overhead.
As for what this a part of the pipeline means, for engineering, it simply means you need to clear up the messy human queries and switch them into one thing that has the next hit price.
For the enterprise and search engine optimization individuals on the market, it means these human queries you’ve been optimizing for are getting remodeled into extra robotic, document-shaped ones.
search engine optimization, as I perceive it, used to care lots about matching the precise long-tail phrase in titles and headings. If somebody looked for “finest trainers for unhealthy knees,” you’d follow that precise string.
What it is advisable to care about now can be entities, attributes, and relationships.
So, if a person asks for “one thing for dry pores and skin,” the rewrites would possibly embrace issues like “moisturizer,” “occlusive,” “humectant,” “ceramides,” “fragrance-free,” “keep away from alcohols” and never simply “how would I discover a good product for dry pores and skin.”
However let’s be clear so there’s no confusion: we are able to’t see the interior rewrites themselves, so these are simply examples.
In case you’re on this half, you’ll be able to dig deeper. I guess there are many papers on the market on how to do that nicely.
Let’s transfer on to what these optimized queries are literally used for.
Utilizing engines like google (for doc degree discovery)
It’s fairly widespread information by now that, to get up-to-date solutions, most AI bots depend on conventional engines like google. That’s not the entire story, but it surely does lower the online all the way down to one thing smaller to work with.

I’m assuming the total net is just too massive, too noisy, and too fast-changing for an LLM pipeline to drag uncooked content material straight. So by utilizing already established engines like google, you get a option to slender the universe.
In case you take a look at bigger RAG pipelines that work with tens of millions of paperwork, they do one thing related. I.e. utilizing a filter of some kind to resolve which paperwork are essential and price additional processing.
For this half, we do have proof.
Each OpenAI and Anthropic have stated they use third-party engines like google like Bing and Courageous, alongside their very own crawlers.
Perplexity could have constructed out this half on their very own by now, however at first, they’d have executed the identical.
We even have to think about that conventional engines like google like Google and Bing have already solved the toughest issues. They’re a longtime expertise that handles issues like language detection, authority scoring, area belief, spam filtering, recency, geo-biasing, personalization, and so forth.
Throwing all of that away to embed your complete net your self appears unlikely. So I’m guessing they lean on these techniques as a substitute of rebuilding them.
Nonetheless, we don’t know what number of outcomes they really fetch per question, whether or not it’s simply the highest 20 or 30. One unofficial article in contrast citations from ChatGPT and Bing, seemed on the rating order, and located that some got here from as far down as twenty second place. If true, this implies it is advisable to goal for top-20-ish visibility.
Moreover, we additionally don’t know what different metrics they use to resolve what surfaces from there. This article argues that AI engines closely favor earned media quite than official websites or socials, so there’s extra happening.
Nonetheless, the search engine’s job (whether or not it’s totally third-party or a mixture) is discovery. It ranks the URL primarily based on authority and key phrases. It’d embrace a snippet of knowledge, however that alone gained’t be sufficient to reply the query.
If the mannequin relied solely on the snippet, plus the title and URL, it will possible hallucinate the small print. That’s not sufficient context.
So this pushes us towards a two-stage structure, the place a retrieval step is baked in — which we’ll get to quickly.
What does this imply by way of search engine optimization?
It means you continue to have to rank excessive in conventional engines like google to be included in that preliminary batch of paperwork that will get processed. So, sure, basic search engine optimization nonetheless issues.
However it might additionally imply it is advisable to take into consideration potential new metrics they may be utilizing to rank these outcomes.
This stage is all about narrowing the universe to some pages price digging into, utilizing established search tech plus inside knobs. Every little thing else (the “it returns passages of knowledge” half) comes after this step, utilizing customary retrieval strategies.
Crawl, chunk & retrieve
Now let’s transfer on to what occurs when the system has recognized a handful of attention-grabbing URLs.
As soon as a small set of URLs passes the primary filter, the pipeline is pretty easy: crawl the web page, break it into items, embed these items, retrieve those that match the question, after which re-rank them. That is what’s known as retrieval.

I name it on-the-fly right here as a result of the system solely embeds chunks as soon as a URL turns into a candidate, then it caches these embeddings for reuse. This half may be new in the event you’re already accustomed to retrieval.
To crawl the web page, they use their very own crawlers. For OpenAI, that is OAI-SearchBot, which fetches the uncooked HTML so it may be processed. Crawlers don’t execute JavaScript. They depend on server-rendered HTML, so the identical search engine optimization guidelines apply: content material must be accessible.
As soon as the HTML is fetched, the content material needs to be changed into one thing searchable.
In case you’re new to this, it’d really feel just like the AI “scans the doc,” however that’s not what occurs. Scanning whole pages per question can be too sluggish and too costly.
As an alternative, pages are cut up into passages, often guided by HTML construction: headings, paragraphs, lists, part breaks, that form of factor. These are known as chunks within the context of retrieval.
Every chunk turns into a small, self-contained unit. Token-wise, you’ll be able to see from Perplexity UI citations that chunks are on the order of tens of tokens, possibly round 150, not 1,000. That’s about 110–120 phrases.
After chunking, these models are embedded utilizing each sparse and dense vectors. This allows the system to run hybrid search and match a question each semantically and by key phrase.
In case you’re new to semantic search, in brief, it means the system searches for which means as a substitute of tangible phrases. So a question like “signs of iron deficiency” and “indicators your physique is low on iron” would nonetheless land close to one another in embedding area. You possibly can learn extra on embeddings right here in the event you’re eager to be taught the way it works.
As soon as a well-liked web page has been chunked and embedded, these embeddings are most likely cached. Nobody is re-embedding the identical StackOverflow reply hundreds of instances a day.
That is clearly why the system feels so quick, most likely the recent 95–98% of the online that really will get cited is already embedded, and cached aggressively.
We don’t know to what extent although and the way a lot they pre-embed to verify the system runs quick for widespread queries.
Now the system wants to determine which chunks matter. It makes use of the embeddings for every chunk of textual content to compute a rating for each semantic and key phrase matching.
It picks the chunks with the best scores. This may be something from 10 to 50 top-scoring chunks.
From right here, most mature techniques will use a re-ranker (cross-encoder) to course of these prime chunks once more, doing one other spherical of rating. That is the “repair the retrieval mess” stage, as a result of sadly retrieval isn’t at all times fully dependable for lots of causes.
Though they are saying nothing about utilizing a cross-encoder, Perplexity is among the few that paperwork their retrieval course of brazenly.
Their Search API says they “divide paperwork into fine-grained models” and rating these models individually to allow them to return the “most related snippets already ranked.”
What does this all imply for search engine optimization? If the system is doing retrieval like this, your web page isn’t handled as one huge blob.
It’s damaged into items (usually paragraph or heading degree) and people items are what get scored. The complete web page issues throughout discovery, however as soon as retrieval begins, it’s the chunks that matter.
Which means every chunk must reply the person’s query.
It additionally signifies that in case your essential info isn’t contained inside a single chunk, the system can lose context. Retrieval isn’t magic. The mannequin by no means sees your full web page.
So now we’ve coated the retrieval stage: the place the system crawls pages, chops them into models, embeds these models, after which makes use of hybrid retrieval and re-ranking to drag out solely the passages that may reply the person’s query.
Doing one other move & handing over chunks to LLM
Now let’s transfer on to what occurs after the retrieval half, together with the “persevering with to go looking” characteristic and handing the chunks to the primary LLM.

As soon as the system has recognized just a few high-ranking chunks, it has to resolve whether or not they’re ok or if it must hold looking out. This choice is sort of definitely made by a small controller mannequin, not the primary LLM.
I’m guessing right here, but when the fabric seems to be skinny or off-topic, it might run one other spherical of retrieval. If it seems to be stable, it might probably hand these chunks over to the LLM.
In some unspecified time in the future, that handoff occurs. The chosen passages, together with some metadata, are handed to the primary LLM.
The mannequin reads all of the offered chunks and picks whichever one finest helps the reply it needs to generate.
It doesn’t mechanically comply with the retriever’s order. So there’s no assure the LLM will use the “prime” chunk. It might favor a lower-ranked passage just because it’s clearer, extra self-contained, or nearer to the phrasing wanted for the reply.
So similar to us, it decides what to soak up and what to disregard. And even when your chunk scores the best, there’s no assurance it is going to be the primary one talked about.
What to assume about
This technique isn’t actually a black field. It’s a system individuals have constructed handy the LLMs the fitting info to reply a person’s query.
It finds candidates, splits paperwork into models, searches and ranks these models, after which fingers them over to an LLM to summarize. So once we perceive how the system works, we are able to additionally determine what we’d like to consider when creating content material for it.
Conventional search engine optimization nonetheless issues lots, as a result of this technique leans on the previous one. Issues like having a correct sitemap, simply rendered content material, correct headings, area authority, and correct last-modified tags are all essential to your content material to be sorted accurately.
As I identified, they could be mixing engines like google with their very own expertise to resolve which URLs get picked, which is price maintaining in thoughts.
However I believe paragraph degree relevance is the brand new leverage level.
Possibly this implies answer-in-one-chunk design will rule. (Simply don’t do it in a means that feels bizarre, possibly a TL;DR.) And keep in mind to make use of the fitting vocabulary: entities, attributes, relationships, like we talked about within the question optimization part.
construct a “GEO Scoring System” (for enjoyable)
To determine how nicely your content material will do, we’ll must simulate the hostile surroundings your content material will dwell in. So let’s attempt to reverse engineer this pipeline.
Observe, that is non-trivial, as we don’t know the interior metrics they use, so consider this as a blueprint.
The concept is to create a pipeline that may do question rewrite, discovery, retrieval, re-ranking and an LLM choose, after which see the place you find yourself in comparison with your rivals for various matters.

You start with just a few matters like “hybrid retrieval for enterprise RAG” or “LLM analysis with LLM-as-judge,” after which construct a system that generates pure queries round them.
Then you definately move these queries by an LLM rewrite step, as a result of these techniques usually reformulate the person question earlier than retrieval. These rewritten queries are what you really push by the pipeline.
The primary examine is visibility. For every question, take a look at the highest 20–30 outcomes throughout Courageous, Google and Bing. Observe whether or not your web page seems and the place it sits relative to rivals.
On the similar time, gather domain-level authority metrics (Moz DA, Ahrefs DR, and many others.) so you’ll be able to fold that in later, since these techniques most likely nonetheless lean closely on these indicators.
In case your web page seems in these first outcomes, you progress on to the retrieval half.
Fetch your web page and the competing pages, clear the HTML, cut up them into chunks, embed these chunks, and construct a small hybrid retrieval setup that mixes semantic and key phrase matching. Add a re-ranking step.
Someplace right here you additionally inject the authority sign, as a result of higher-authority domains realistically get scored increased (despite the fact that we don’t know precisely how a lot).
After you have the highest chunks, you add the ultimate layer: an LLM-as-a-judge. Being within the prime 5 doesn’t assure quotation, so that you simulate the final step by handing the LLM just a few of the top-scored chunks (with some metadata) and see which one it cites first.
Once you run this to your pages and rivals, you see the place you win or lose: the search layer, the retrieval layer or the LLM layer.
Bear in mind that is nonetheless a tough sketch, but it surely provides you one thing to begin with if you wish to construct an analogous system.
This text centered on the mechanics quite than the technique facet of search engine optimization/GEO, which I get gained’t be for everybody.
The purpose was to map the circulate from a person question to the ultimate reply and present that the AI search software isn’t some opaque drive.
Even when elements of the system aren’t public, we are able to nonetheless infer an inexpensive sketch of what’s taking place. What’s clear thus far is that the AI net search doesn’t exchange conventional engines like google. It simply layers retrieval on prime of them.
Earlier than ending this, it’s price mentioning that the deeper analysis characteristic is totally different from the built-in search instruments, that are pretty restricted and low-cost. Deep analysis possible leans on extra agentic search, which can be “scanning” the pages to a higher extent.
This would possibly clarify why my very own content material from my web site exhibits up in deep analysis despite the fact that it’s not optimized for the essential search layer, so it virtually by no means exhibits up in primary AI search.
There’s nonetheless extra to determine earlier than saying what really issues in follow. Right here I’ve largely gone by the technical pipeline but when that is new stuff I hoped it clarify it nicely.
Hopefully it was simple to learn. In case you loved it, be at liberty to share it or join with me on LinkedIn, Medium or by my site.
❤