A robotic looking for employees trapped in {a partially} collapsed mine shaft should quickly generate a map of the scene and establish its location inside that scene because it navigates the treacherous terrain.
Researchers have not too long ago began constructing highly effective machine-learning fashions to carry out this advanced process utilizing solely pictures from the robotic’s onboard cameras, however even the very best fashions can solely course of a number of pictures at a time. In a real-world catastrophe the place each second counts, a search-and-rescue robotic would wish to shortly traverse giant areas and course of 1000’s of pictures to finish its mission.
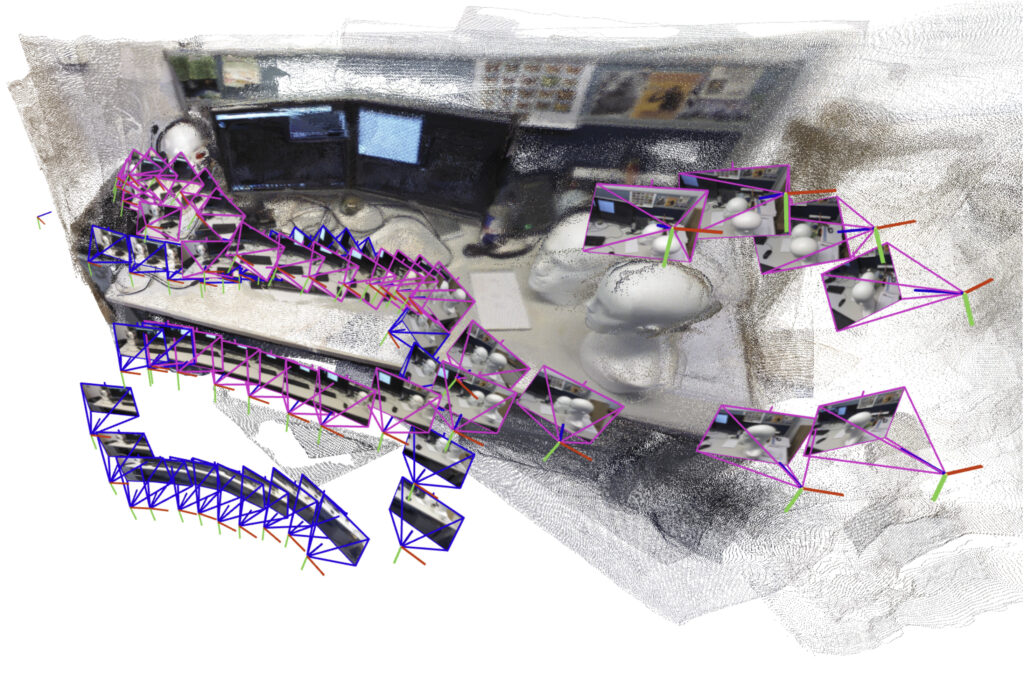
To beat this drawback, MIT researchers drew on concepts from each current synthetic intelligence imaginative and prescient fashions and classical laptop imaginative and prescient to develop a brand new system that may course of an arbitrary variety of pictures. Their system precisely generates 3D maps of sophisticated scenes like a crowded workplace hall in a matter of seconds.
The AI-driven system incrementally creates and aligns smaller submaps of the scene, which it stitches collectively to reconstruct a full 3D map whereas estimating the robotic’s place in real-time.
Not like many different approaches, their method doesn’t require calibrated cameras or an knowledgeable to tune a fancy system implementation. The easier nature of their method, coupled with the velocity and high quality of the 3D reconstructions, would make it simpler to scale up for real-world purposes.
Past serving to search-and-rescue robots navigate, this methodology might be used to make prolonged actuality purposes for wearable gadgets like VR headsets or allow industrial robots to shortly discover and transfer items inside a warehouse.
“For robots to perform more and more advanced duties, they want rather more advanced map representations of the world round them. However on the identical time, we don’t wish to make it more durable to implement these maps in observe. We’ve proven that it’s attainable to generate an correct 3D reconstruction in a matter of seconds with a software that works out of the field,” says Dominic Maggio, an MIT graduate pupil and lead writer of a paper on this method.
Maggio is joined on the paper by postdoc Hyungtae Lim and senior writer Luca Carlone, affiliate professor in MIT’s Division of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AeroAstro), principal investigator within the Laboratory for Data and Determination Programs (LIDS), and director of the MIT SPARK Laboratory. The analysis will probably be introduced on the Convention on Neural Data Processing Programs.
Mapping out an answer
For years, researchers have been grappling with a vital component of robotic navigation known as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). In SLAM, a robotic recreates a map of its setting whereas orienting itself throughout the house.
Conventional optimization strategies for this process are likely to fail in difficult scenes, or they require the robotic’s onboard cameras to be calibrated beforehand. To keep away from these pitfalls, researchers practice machine-learning fashions to study this process from information.
Whereas they’re easier to implement, even the very best fashions can solely course of about 60 digital camera pictures at a time, making them infeasible for purposes the place a robotic wants to maneuver shortly by way of a various setting whereas processing 1000’s of pictures.
To resolve this drawback, the MIT researchers designed a system that generates smaller submaps of the scene as a substitute of the complete map. Their methodology “glues” these submaps collectively into one general 3D reconstruction. The mannequin remains to be solely processing a number of pictures at a time, however the system can recreate bigger scenes a lot quicker by stitching smaller submaps collectively.
“This appeared like a quite simple resolution, however after I first tried it, I used to be stunned that it didn’t work that effectively,” Maggio says.
Trying to find a proof, he dug into laptop imaginative and prescient analysis papers from the Eighties and Nineties. By this evaluation, Maggio realized that errors in the way in which the machine-learning fashions course of pictures made aligning submaps a extra advanced drawback.
Conventional strategies align submaps by making use of rotations and translations till they line up. However these new fashions can introduce some ambiguity into the submaps, which makes them more durable to align. As an example, a 3D submap of a one aspect of a room might need partitions which might be barely bent or stretched. Merely rotating and translating these deformed submaps to align them doesn’t work.
“We’d like to ensure all of the submaps are deformed in a constant approach so we are able to align them effectively with one another,” Carlone explains.
A extra versatile method
Borrowing concepts from classical laptop imaginative and prescient, the researchers developed a extra versatile, mathematical method that may signify all of the deformations in these submaps. By making use of mathematical transformations to every submap, this extra versatile methodology can align them in a approach that addresses the paradox.
Based mostly on enter pictures, the system outputs a 3D reconstruction of the scene and estimates of the digital camera areas, which the robotic would use to localize itself within the house.
“As soon as Dominic had the instinct to bridge these two worlds — learning-based approaches and conventional optimization strategies — the implementation was pretty simple,” Carlone says. “Developing with one thing this efficient and easy has potential for lots of purposes.
Their system carried out quicker with much less reconstruction error than different strategies, with out requiring particular cameras or further instruments to course of information. The researchers generated close-to-real-time 3D reconstructions of advanced scenes like the within of the MIT Chapel utilizing solely brief movies captured on a mobile phone.
The common error in these 3D reconstructions was lower than 5 centimeters.
Sooner or later, the researchers wish to make their methodology extra dependable for particularly sophisticated scenes and work towards implementing it on actual robots in difficult settings.
“Understanding about conventional geometry pays off. In case you perceive deeply what’s going on within the mannequin, you will get significantly better outcomes and make issues rather more scalable,” Carlone says.
This work is supported, partially, by the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis, U.S. Workplace of Naval Analysis, and the Nationwide Analysis Basis of Korea. Carlone, at the moment on sabbatical as an Amazon Scholar, accomplished this work earlier than he joined Amazon.